Role Of Technologies in Inventory Management


Technologies in inventory management help get a competitive advantage by optimizing the use of resources, increasing customer satisfaction, conducting detailed analysis, and minimizing losses. Therefore, 88% of retailers plan to upgrade their inventory by integrating new-age digital solutions like live-time tracking, detailed analytics, and data-driven demand forecasting.

In the post below, you will discover how emerging technologies in inventory management help optimize warehousing and improve customer experience. Also, you will learn more about essential and advanced inventory management technologies to adopt.
Essential Technologies Used In Inventory Management
It’s impossible to underestimate the important role of technologies in inventory management and warehouse maintenance. They help facilitate the process of goods ordering, storing, and shipping. Some of them have been widely used by businesses for many years.
1. Warehouse Management Software
These days, most digital solutions have the form of warehouse management software (WMS). It is a kind of information technology in inventory management software with many features for seamless item ordering, storing, and shipping. It helps get rid of the need to use paper spreadsheets to keep track of every action.
Warehouse management software can be custom or ready-made. Also, a digital solution can be on-premises or cloud-based. It can have a lot of different features aimed to solve several problems of businesses.
The key features of a warehouse management system are the following:
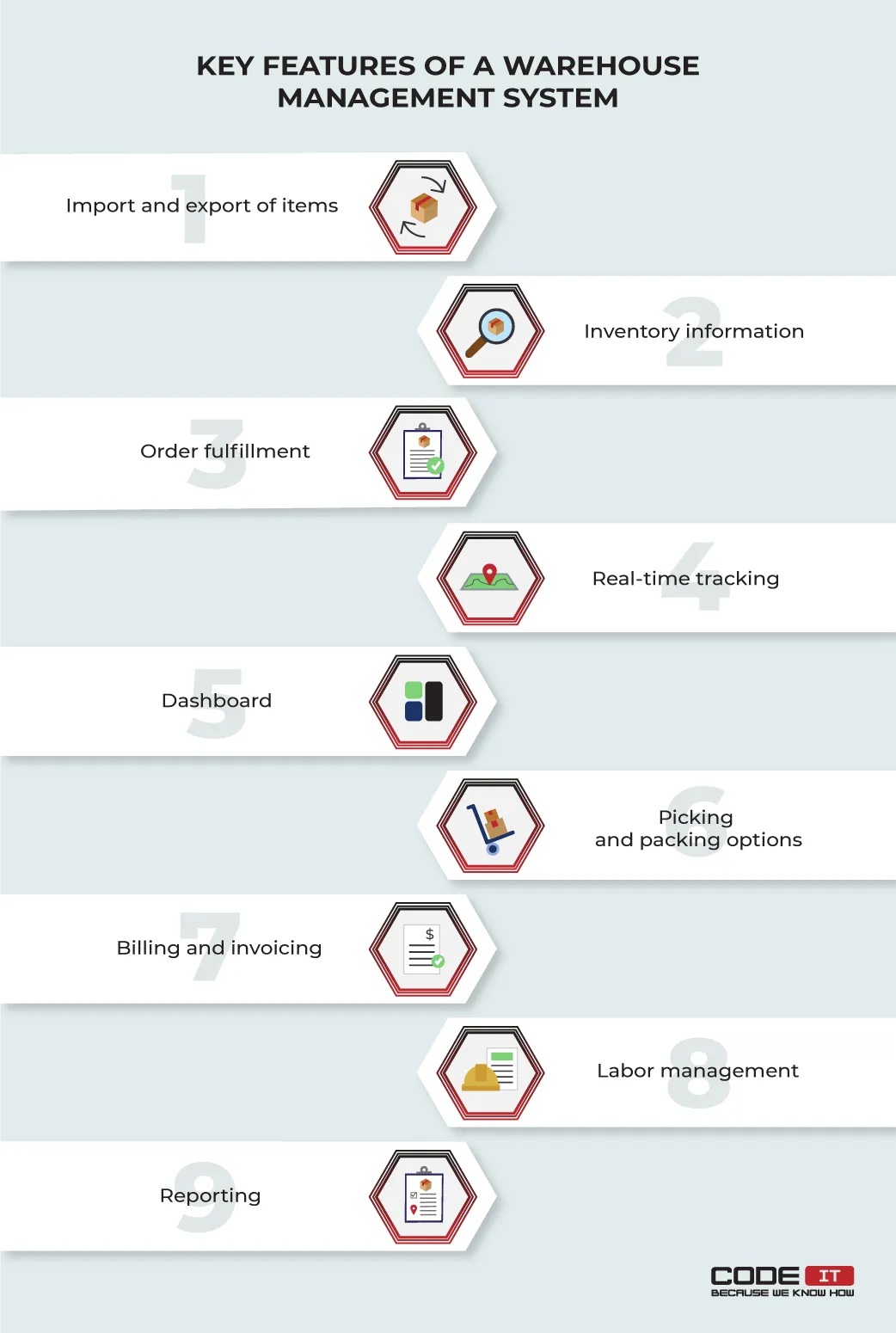
1.1. Import and export of items
Indeed, an inventory management system should provide the opportunity to add products to a database manually. However, it should also be capable of importing and exporting many items to a database using a comma-separated values (CSV) file.
1.2. Inventory information
It is an essential feature for WMSs to track all the items. Data can be entered and updated manually or automatically. Inventory information can imply a lot of details like stock keeping unit (SKU) codes, name, availability, number of items, size, price, image, arrival date, etc.
1.3. Order fulfillment
A WMS needs to store information about clients and other crucial details to deliver goods fast. It helps properly organize reserving to speed-up cargo loading and shipping. Besides, the order fulfillment functionality helps manage returns.
1.4. Real-time tracking
It’s vital to get accurate information on items stored in a warehouse. Real-time inventory tracking can help monitor all the processes efficiently and update them effectively upon the need. Real-time data facilitates warehouse management because managers can monitor all the processes remotely from one place.
1.5. Dashboard
The proper use of technologies in inventory management can help consume data conveniently. Moreover, a dashboard can be configured for different roles. Consequently, various users get access to insights arranged in different order to facilitate every user’s work.
1.6. Picking and packing options
A warehouse management system should provide detailed information on the types of items and how they need to be packed. For instance, fragile or expensive tech items must be packed well to be safely delivered. Moreover, a WMS needs to comprise information on how a customer will pick up a delivery.
1.7. Billing and invoicing
A WMS should have the billing and invoicing functionality to send quotes, receive invoices, and manage all payments. Also, it should hold information about all the transactions securely.
1.8. Labor management
To run warehousing processes smoothly, a WMS should be capable of assigning tasks to workers. Also, it needs to help track the performance of employees with the help of key performance indicators (KPIs).
1.9. Reporting
A WMS should have an inventory reporting feature to get valuable inventory management insights. A system needs to analyze large amounts of raw data gathered about a warehouse using custom algorithms to help businesses get detailed reports and data-driven forecasts.
Developers and businesses constantly come up with innovative ideas for inventory management systems, so they build a large assortment of useful features for efficient supply chain management (SCM). Therefore, you can develop a system that has a lot of useful and custom-designed features to facilitate warehouse management.
Let’s Build A Custom Warehouse Management System

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
2. Barcode System
Barcodes are one of the most popular types of technologies in inventory management because they help make item tracking less time-consuming. A barcode is an image that helps assign a unique value that holds certain information to any item. Since a barcode is unique and can be scanned in less than a second, the system helps facilitate inventory management significantly.
Businesses can create custom barcodes that contain the required information and print them to facilitate inventory management. There are two types of barcodes:
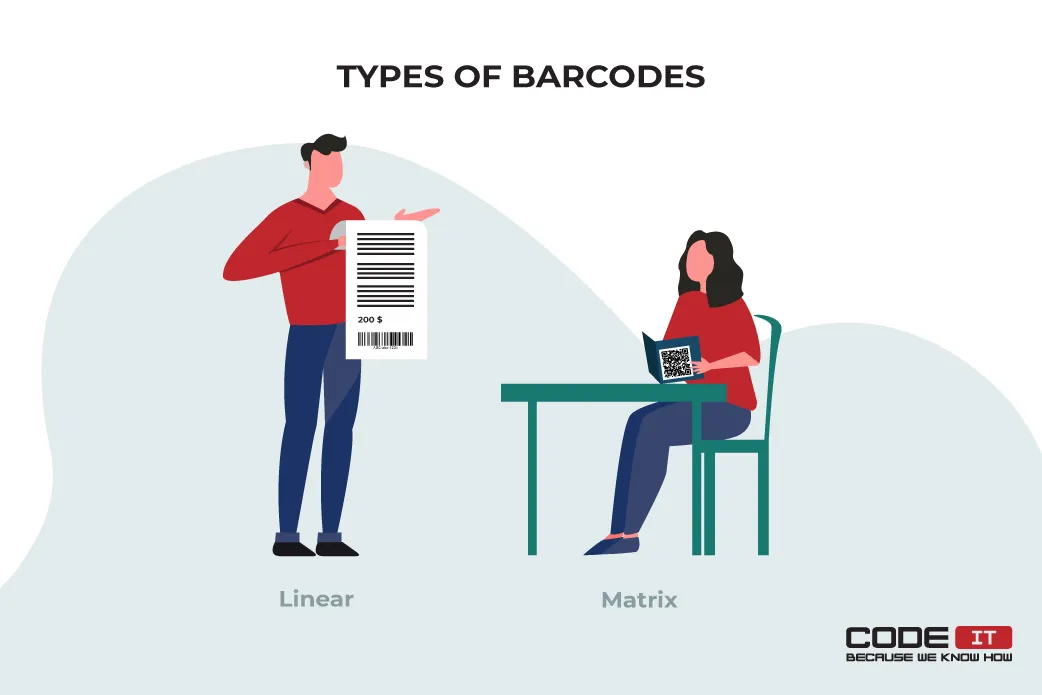
2.1 Linear
It is the most widespread type of barcode that has been used since 1951. It is a one-dimensional type of barcode that has the form of vertical lines arranged in a certain order. Moreover, it implies digits for manual barcode input.
Different kinds of linear barcodes can hold various amounts of data. The most common information types that a linear barcode can keep are the following:
- SKU number
- Name
- Weight
- Manufacturing and expiry date
- Manufacturer’s name
2.2 Matrix
It is an upgraded type of barcode that was introduced in 1994. The most popular type of matrix barcode is the Quick Response (QR) code. It is a two-dimensional type of barcode that can hold more information than linear barcodes. Nevertheless, it has additional benefits that are the following:
- 360-degree scanning
- Low background contrast requirements
- Automatic error correction
- Any scanning distance
QR codes are one of the most popular types of matrix barcodes. They are divided into two types:
- Static – A code cannot be changed once it is printed. Users get the same information when scanning a static QR code.
- Dynamic – A QR code contains a link that leads a user to a certain resource. Information fetched from an external resource can be updated, which is convenient for real-time tracking and more efficient inventory management.
The most common type of data that a matrix barcode can hold are:
- URL
- SKU number
- Name
- Weight
- Text data
Barcodes can be read by scanners or mobile apps that use the devices’ cameras. Also, managers can input the digits from linear barcodes to WMSs if there is no option to use a scanner.
3. RFID Technology
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) is a technology that helps enhance inventory management by using radio waves. Every item gets a unique RFID tag that stores data and can be easily scanned.
This wireless technology used in inventory management helps increase productivity because many tags can be read automatically. Therefore, the use of radio-frequency identification tags is one of the top trends in inventory management because of real-time tracking and fast information updates.
Inventory management technology requires a business to install antenna, reader, and RFID tags on assets. The system foresees the opportunity to write information to chips and read it wirelessly. The minimum distance to a chip may vary from a few to thirty feet. There are two types of RFID chips:
- Active – An expensive and less popular type of RFID tag that requires a source of energy to transmit radio waves.
- Passive – Radio waves transmitted by an antenna generate current in a tag, so it can receive, update, and send information. It is the most popular type of RFID tag.
The data that can be updated facilitates real-time tracking. It is worth noting that the serial number of RFID tags is the only information that cannot be updated.
The RFID technology for inventory management helps find a product in a warehouse quickly because all the information about moving assets can be tracked and stored in a database. An RFID tag can store up to 2 kilobytes (KBs) of data. The most common data types that an RFID tag holds are the following:
- Serial RFID tag’s number
- SKU number
- Serial product’s number
- Name
- Location
- Weight
4. LiFi Technology
The light fidelity (LiFi) technology is an alternative to a WiFi network. The technology uses sources of light and sensors to transmit information. It offers the opportunity to connect more devices into one system.
The light source is generated by LED bulbs that update the frequency to transmit data in the form of light. The frequency changes are not visible to the human eye. It is widely used for building warehouse networks because this technology can connect many types of devices without any issues. Also, the inventory management technology is applied for 3D positioning for robots.
What Is Inventory Management And How Tech Makes An Impact
Inventory management is a complicated process that requires keeping the correct number of items in a warehouse to avoid product shortages or oversupplies. Moreover, it requires managing all the processes effectively to deliver items fast, overcome competitors, and keep recurring clients.
Usually, businesses use warehouse management systems (dedicated inventory software) to keep track of their inventory. Digital WMSs are advanced enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions.
The role of inventory management and information technology in a supply chain is vital. Inventory management features help companies that operate in the logistics niche achieve the following:
- Optimized resources usage
- Enhanced customers satisfaction
- Automated inventory management
- Data-driven analytics
- Reduced product delivery time
- Lowered operational expenses
- Minimized fraud and theft
Many types of inventory management techniques are applied to track all items and maintain a consistent supply chain. The top three are the following:
- Push strategy – Items are delivered from a manufacturer to a warehouse. To not run out of stock, retailers need to forecast the approximate number of products to store.
- Pull strategy – A store or warehouse requests products from suppliers when clients order them. Usually, this technique is applied to custom or expensive items.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) strategy – A warehouse stores the minimum number of items. All extra requests get processed by applying the pull strategy, which may cause delivery delays.
Nevertheless, there are also other inventory management strategies:
- Dropshipping – Product management and shipment are delegated to a third-party company that has a large warehouse.
- Bulk shipment – Products get purchased in bulk to avoid shortage and get a discount.
- Cross-docking – Items get sorted and shipped simultaneously after being delivered to a warehouse. The strategy eliminates the need to hold products.
- Consignment – A supplier delivers a certain number of products without upfront payments. A retailer pays for products only when they are sold to customers.
- Cycle counting – A small variety of items get counted on certain days. It helps monitor the number of different product groups left effectively.
Need to revamp warehousing?

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
Types Of Inventory Management Systems
Inventory management can be performed in different ways, applying various approaches. Moreover, the type of workflow depends on the technologies used. The foremost types of inventory control systems that businesses use are as follows.
1. Spreadsheet-based
It is a baseline inventory management approach involving manual counting and spreadsheet-based inventory management systems. All the records are calculated using in-built tools for data analysis and visualization.
Implementing a spreadsheet-based IMS is quick and easy. However, it is labor-intensive and prone to human error. Also, digital spreadsheets have record limitations, making it challenging to process large amounts of data.
2. Cloud-based
The usage of cloud-based inventory management software helps streamline processes, enabling access to the right amount of storage and computing resources. It unlocks integration opportunities, streamlining workflows, and automated data-sharing. Also, businesses need to pay for the computing power they use only, eliminating expenses for infrastructure idling time.
A stable internet connection is required for running a cloud-based infrastructure since servers are owned and managed by a third-party provider.
3. Automated
Automated inventory management systems leverage cross-platform integrations, custom user agents, and IoT infrastructure to collect and analyze data automatically. Fully-automated systems help monitor inventory in real time and manage items across multiple locations effectively.
It reduces the risks of manual errors, streamlines data management, and unlocks complete inventory visibility. These systems serve as powerful asset inventory management tools, providing better accuracy and efficiency. However, implementing a fully automated system requires a high initial investment and top-tier expertise for developing new solutions and custom integrations.
4. Mobile-based
Mobile-optimized graphical user interface helps employees to seamlessly access the functionality of an inventory management system. Workers can improve their productivity by using tablets or mobile devices that they can carry and utilize remotely. This approach is often an extension of periodic inventory management systems or basic stock management systems, allowing flexibility for on-the-go operations.
Manual vs. Tech-Advanced Inventory Management
Let’s explore the min/max inventory management approaches, highlighting the differences between manual and technologically advanced IMS.
| Manual | Tech-advanced | |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Traditional methods of inventory tracking and physical inventory count. The approach involves manual item counting and setting min/max levels to trigger replenishment. | A technologically advanced inventory management. The usage of IoT, AI, cloud computing, barcode scanning, and other technologies to automate operations and enable instant visibility. |
| Advantages | Low cost Easy to implement Flexibility | Real-time tracking Warehouse automation and accuracy Reduced costs and errors Easy to scale Predictive analytics Improved inventory valuation and sales decisions Smarter purchasing |
| Disadvantages | Manual error Time-consuming Poor scalability No real-time data | High implementation cost Complexity of maintenance |
Manual inventory management example
A company’s employees manually observe the in-stock inventory by conducting physical inventory count and cycle counting. All the data is recorded on paper and further moved to digital spreadsheets. Item replenishment activities are triggered when inventory reaches the minimum level.
Tech-advanced inventory management example
An enterprise-grade e-commerce company uses radio frequency identification (RFID) tags to track inventory in real time. Smart cameras identify and track activities. Actuators and automated guided vehicles enable automated item picking, packing, and transportation. All the data is sent to the cloud server and becomes available simultaneously to different departments.
Rising Trends In Inventory Management
Let’s discover how technology aided inventory management with new advancements. The new technology for inventory management of the future are as follows.
1. Internet of Things
The Internet of things (IoT) is a concept of developing systems capable of connecting different types of devices. Various technologies integrated into one system can facilitate inventory management optimization and warehouse monitoring by gathering different information types in one place.
The variety of IoT devices is wide. Most have the “smart” prefix to highlight the devices’ capabilities of transmitting data over a network and being managed remotely by people or other digital systems.
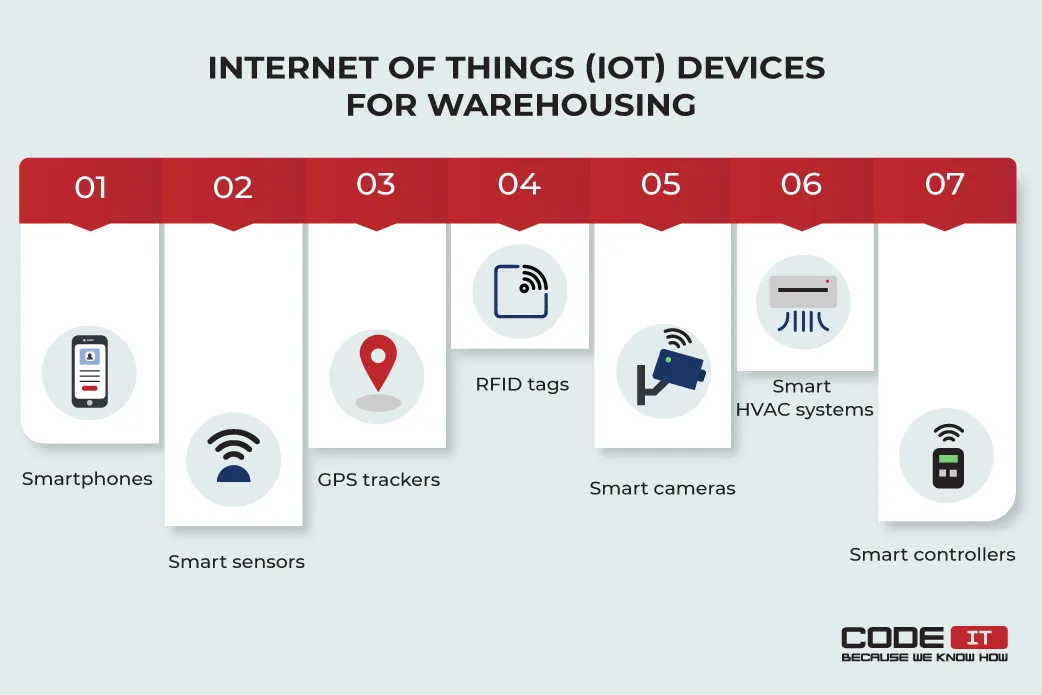
The most popular types of IoT technologies in inventory management are:
- Smartphones
- Smart sensors
- GPS trackers
- RFID tags
- Smart cameras
- Smart HVAC systems
- Smart controllers
The implication of IoT technologies like smart sensors and controllers helps automate a lot of processes and improve management. For instance, IoT devices can measure the temperature or moisture in a warehouse and adjust the HVAC system to keep the required condition automatically.
Application example: A company uses IoT-driven technologies like smart cameras, GPS trackers, and RFID tags to track inventory in real-time. Using the data received from sensor companies can automatically monitor the location and condition of goods.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are the leading technologies that can process a large amount of data and perform some human-like actions. AI can recognize the speech or analyze videos captured by cameras. Machine learning can identify patterns in the supply chain to automate labor force and assets management. For instance, it can analyze workers’ behavior or incorrect placement of items.
However, in most cases, the technologies are used for analyzing data and getting valuable insights. AI helps get data-driven demand forecasts and predictive planning. The report prepared by McKinsey & Co states that AI-enabled supply-chain management can help cut logistics costs by 15%.
Application example: A chain of grocery stores uses an AI-driven system trained on a wide variety of data, including sales records, local events, weather forecasts, etc. The insights gained are used to optimize replenishment strategies based on future customer demand. The system helps order the right number of perishable products, reducing the wastage rate.
3. Cloud Infrastructure
The cloud technology impacts just-in-time inventory management by enabling simultaneous access to data from any location—via the Internet. The cloud-based infrastructure is easy to set up and scale up. Businesses can seamlessly adjust the storage space and computing power of their servers. The single cloud infrastructure makes it easy for large enterprises to sync their inventory data across multiple facilities located in different locations.
Application example: A global manufacturing company uses a cloud-based inventory management system to synchronize all the data across multiple production sites. It enables C-level executives to access all the information in one place remotely at any time. It helps stay updated about all the processes, improve coordination between departments, and receive real-time alerts.
4. Automated Picking Tools
Enterprise-grade businesses that need to manage an enormous number of items in their warehouses integrate automated picking tools. Such systems use robotic manipulators, barcodes, or RFID tags to pick all the assets automatically. The technology helps reduce operating costs, enhance productivity, and minimize human error chance.
Application example: A logistics company uses robotic arms for automated item picking. The system automatically scans RFID tags on packages and picks and sorts items for shipment. Hence, the company has automated bothersome operations, tackling large numbers of items efficiently.
5. Automated Guided Vehicles
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are usually small devices that help move items in a warehouse from one location to another. It is an advanced inventory management technology that helps replace the need to have a lot of vehicles and drivers to move assets in a warehouse. AGVs work autonomously and can perform monotonous tasks 24/7. They navigate using floor stickers, LiFi technology, vision cameras, or wires.
Application example: An enterprise has implemented AVGs to transport racks in a warehouse automatically. The AGVs navigate using vision cameras and floor markers. The technology helps reduce the required manual input for transporting goods in a warehouse—the employees are focused on sorting items and collecting orders at defined locations.
6. Blockchain
Blockchain is a great technology that is used in many industries. It has become trendy in the financial sector because the distributed data management approach helps make secure and transparent transactions.
The adoption of blockchain positively impacts information technology in inventory management. By adopting blockchain, businesses can enhance the security of their warehouse management systems and make safe transactions. It’s tough to hack blockchain-driven systems.
Application example: A company uses blockchain technology to secure its inventory transactions. This helps prevent the purchase of counterfeit products and builds trust with clients.
7. Predictive Analytics
The analysis of historical inventory data helps predict future demand changes, including seasonal spikes/drops. Predictive analytics run by custom algorithms help ensure smooth inventory management, avoiding stockouts and overstocking.
Application example: An e-commerce company integrates business intelligence tools to analyze large datasets of sales to predict future demand changes. The insights help adjust item purchasing strategies to meet seasonal demand changes.
8. Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) is utilized for employee guidance and support, helping improve the performance of the labor force. AR glasses overlay the physical environment with digital objects, helping employees understand what items to pick or where to put items in a warehouse.
Application example: A company has provided its warehouse workers with AR glasses. They guide workers to the correct locations and provide real-time instructions. The inventory management technology helps reduce human error, improve picking accuracy, and decrease the training time for new employees.
9. Third-Party Integration
Integrating software from external vendors helps enrich the functionality of the existing IMS. Using application programming interfaces (APIs) helps sync inventory data with other systems securely and automatically get responses from third parties.
Application example: An online marketplace uses an API to integrate shipping software from an external provider. The system enables automatic synchronization with multiple couriers, allowing users to track packages accurately and automatically share delivery updates with customers.
Challenges Of Inventory Management Systems
A business must tackle many challenges to successfully implement a custom inventory management system. This includes implementing cross-system integration for continuous data collection and developing smart algorithms to interpret it correctly.
| Challenge | How We Solve |
|---|---|
| Isolated solutions | Build custom data-sharing pipelines, enabling smooth cross-system communication. Moreover, we implement data validation tools to ensure no pieces of information are missed or changed. |
| Diverse integration requirements | Develop a custom data mapping tool that automatically transforms data, matching the unique integration requirements. |
| Demand forecasting accuracy | Implement a machine learning model and train it using historical data. Clean and validate the data used for training to eliminate outliners, missing entries, or irrelevant data. Also, involve a data scientist to understand the real meaning of ML outcomes for better model fine-tuning. |
| Tech stack limitations | Identify the bottlenecks and refactor legacy systems to fix the issue and ensure future growth. |
| Human factor | Automate workflows and build cross-system integrations, eliminating the need to manually input data. Also, develop additional validation tools that highlight possible errors and offer improvement suggestions. |
| Multiple location management | Establish a main server with real-time connections to the company-wide network of IoT devices. Enable a centralized inventory monitoring and management approach. |
1. Isolated Solutions
Workers must manually input records due to a lack of cross-platform data pipelines or the use of isolated solutions, which can lead to potential errors. For example, they may misspell item names, leading to duplicate inventory records or input incorrect item numbers, locations, etc. This can result in inaccurate records that disrupt operations.
2. Diverse Integration Requirements
Automation implementation requires businesses in the logistics industry to integrate multiple digital systems from various vendors. Moreover, digital solutions may utilize various data formats, making it challenging to develop cross-system data-sharing pipelines. In some cases, it’s required for companies to develop and implement additional data validation and transformation solutions to enable automation in an organization.
3. Demand Forecasting Accuracy
The accurate prediction of future demand requires analyzing historical datasets, seasonal trend change patterns, and unforeseen events. Consequently, organizations have to collect and prepare large amounts of data from various sources.
Implementing an ML-driven solution helps overcome the limitations of traditional mathematical algorithms by leveraging the technology’s capabilities to identify hidden patterns. The development and implementation of machine learning algorithms for demand forecasting require niche-specific expertise.
4. Tech Stack Limitations
Cross-system communication, advanced analysis solutions, and real-time data processing can be implemented when all systems can communicate seamlessly. However, in some cases, businesses may utilize legacy software built using outdated technologies. In such a case, the refactoring of the existing applications may be required.
Also, it might be challenging to identify data sources in each system. As a consequence, business analysis experts have to thoroughly examine the existing solutions to map out all the data sources.
5. Human Factor
Workers play a crucial role in digitalizing inventory management operations. They must grasp a significant amount of information by exploring and studying manual documentation. To overcome this issue, it’s advisable to create a detailed worker re-skilling plan that includes scheduled learning sessions, educational materials, workshops, and other relevant resources.
One of the pitfalls that need to be considered when planning digital solution implementation is employees’ possible resistance to switching from tried-and-tested workflows. This resistance can also affect the speed of tasks such as stock picking time, further delaying operations.
6. Multiple Location Management
With multiple storage locations and complex warehouse layouts, an organization needs to utilize a centralized solution that synchronizes data in real time. The architecture of cross-warehouse management systems gets more complex when a business has inconsistent storage layouts and needs to tackle slow-moving inventory. Additionally, theft and spoilage can occur when items are stored inefficiently or when warehouse environments lack proper monitoring.
When To Upgrade Your Inventory Management System
Upgrading the existing IMS and implementing new technologies need organizations to invest a sustainable amount of time and money. The advantages of using accurate inventory control and automation outweigh the efforts in many cases, including these ones.
1. Inefficient Workflows
Upgrade your operations with custom digital solutions if your business is struggling with inefficient, manual workflows. Start by implementing an automated barcode inventory management system to enable complete visibility of your inventory. Automating repetitive tasks will help reduce the chance of error and enhance efficiency.
2. Fast Business Scaling
It’s challenging to scale your business fast when using a periodic inventory system. A limited number of employees can hardly tackle an overwhelming number of orders, new products, bulk orders, etc.
The use of centralized and cloud-based inventory software helps organize processes. Cloud-based inventory software can be easily scaled, matching a business’s ever-changing demands. Moreover, the integration with third-party solutions enables automated data exchange for better inventory information fetching and sharing.
3. Information Update Delays
Implementing custom solutions that gather data from IoT devices and send it to the main server simultaneously can solve issues such as inconsistent data across platforms and lags in data updates. Business intelligence solutions also help promptly analyze the data, delivering real-time inventory management insights in the form of dashboards and custom reports.
4. High Inventory Holding Costs
The lack of inventory visibility and poor planning can lead to increased inventory holding costs. Furthermore, it can cause inventory piling up and increased wastage. Businesses that utilize advanced analytics solutions develop accurate demand forecasting based on historical data, repairing events, seasonal changes, and other external factors. Using data-backed insights ensures better management of inventory valuation and helps calculate the cost of goods sold (COGS) more effectively.
5. Isolated Solutions Usage
Disconnected systems from different vendors used within an organization need employees to import/export records manually. This method requires labor-intensive operations and leads to data update lags. The development of custom integrations helps enable cross-platform communication, streamline workflows, and enable automation, particularly for e-commerce fulfillment processes.
Tips For Selecting Inventory Management Technologies
Selecting and implementing the right technologies helps streamline inventory management operations and fosters transparency throughout the organization. The following tips will help you build the systems your business really needs and avoid rework.
1. Identify Business Objectives
It’s crucial to clearly define the goals you want to achieve by implementing new technologies. Map out your business processes and identify bottlenecks for developing solutions that deliver real results, unlocking future growth opportunities.
2. Create Software Requirements Specification
Define the features you need to implement and describe their functionality. Plan for integrations, like ERP systems, e-commerce platforms, logistics companies, financial software, etc. Also, outline scalability and flexibility requirements to ensure the sustainable growth of your business.
3. Research Ready-To-Use Components
Streamline new inventory management solution development and implementation by choosing pre-built components, including libraries, SDKs, open-source modules, third-party services, etc. Moreover, pre-built components help proof of concept (PoC) fast for validating an idea.
4. Run Vendor Analysis
Ensure your day-to-day operations and future growth can’t be limited by the capabilities of third-party service providers. Make a thorough analysis of vendors if using pre-built components and systems. Using custom-built or open-source technologies is the best way to avoid vendor lock-in.
Statistics On Adoption Of Technologies In Inventory Management
Indeed, modern technologies help optimize inventory management and make it more efficient. Let’s take a deeper dive into the statistics to discover the benefits of information technologies in inventory management for small businesses and large enterprises.
- 10% of cost reduction – Businesses can cut expenses by eliminating stock-outs and overstocks with the help of smart data analysis and accurate forecasts
- 57% of responders use inventory management systems – Less than half of small companies don’t monitor their inventory or apply the manual management approach instead
- 88% of retailers plan to upgrade – Most supply chain managers don’t want to lose a competitive advantage brought by modern technologies and plan to enhance their warehouses
- 37% of businesses monitor performance – Roughly a third of businesses are concerned about the performance of their warehouses and monitor them constantly to spend resources wisely
- 73% of warehouses plan to adopt mobile devices – Most businesses want to use logistics software installed on mobile devices to facilitate inventory management
CodeIt Expertise
Our team has developed many innovative warehousing and inventory management solutions. Learn more about the two of them, GIObikes and ConnectSx, in more detail.
GIObikes
GIObikes is a fully functional eCommerce platform from scratch that thousands of users use daily.
Problem
The client struggled because of the insufficient functionality offered by eBay to sell products online. He contacted our team, requesting us to develop an innovative platform for switching from eBay to a personal website, keeping eBay’s auctioning functionality.
Solution
We’ve gathered a team of tech experts and selected a tech stack. Also, we’ve created an incremental solution development plan and implemented it. The core components of the web app are as follows.
- Online website — A site launched on a live server capable of managing more than 5,000 active daily users.
- Auction — The opportunity to add new products, share bids, manage auction fees, and buy products now.
- Warehouse management software — A comprehensive software for keeping track of all the items in a warehouse. Items’ location, automatic barcode creation, and out-of-stock alerts are the core features of the inventory management system.
- Affiliate system — The system offers the ability to run affiliate programs automatically. Meanwhile, the admin users have full access to all the information about affiliate programs and their participants.
- Shipping integration — The system offers the opportunity to pick different shipping methods. API-integrated shipping calculators foresee the opportunity to estimate the cost of shipping simultaneously.
- Secure payments — Integrated payment gateways offer the opportunity to make stress-free payments using credit cards, PayPal, or bank wire transfers.
ConnectSx
ConnectSx is a set of web and mobile applications for medical inventory management.
Problem
The client aimed to help clinics resolve poor medical inventory visibility by developing a forward-looking healthcare supply chain management solution. He hired and onboarded the CodeIT team to the existing app development project.
Our team was required to optimize it. Further, we were tasked with ideating a solution, selecting a tech stack, and developing new applications.
Solution
We conducted a technical audit and came up with the best option—to reboot the project. Our team has developed three standalone applications that enable seamless medical inventory management.
- Web inventory management app
- Mobile inventory management app
- Mobile UDI scanning app
The developed applications enable the opportunity to:
- Manage and track medical inventory
- Import data from external systems
- Track medical product expiration dates
- Check inventory usage statistics
- Submit transfer requests
- Scan barcodes using a smartphone
Main Takeaways
The adoption rate of inventory management technology systems rises at a high pace. Technologies help automate many warehouse processes and make data-driven forecasts. Warehouse management and barcode systems are the essential technologies that help keep track of all the items meticulously.
However, there are a lot of advanced technologies that help increase performance and get rid of manual management. Enterprise-grade warehouses actively adopt AI and ML, automated guided vehicles, automated picking tools, and blockchain to deliver products fast and increase customer satisfaction.
FAQ
Various technologies are used to manage inventory and keep track of all the items in a warehouse. The top technologies are:
- Warehouse management software
- Barcode system
- RFID tags
- Internet of things
- LiFi technology
- Artificial intelligence
- Machine learning
- Automated picking tools
- Automated guided vehicles
- Blockchain
Technological inventory is a warehouse management approach focused on adopting new technologies to streamline different processes. The core characteristic of technological inventory is the use of data-driven forecasting, automated picking, barcode system, and digital inventory management.
The top three inventory management techniques are:
- Push strategy
- Pull strategy
- Just-in-Time (JIT) strategy
The fastest-rising trends and new technology for inventory management are as follows.
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- AI and ML
- Cloud infrastructure
- Automated picking
- Automated guided vehicles (AVGs)
- Blockchain
- Predictive analytics
- Augmented reality
- Third-party integration
The foremost statistics that define how technology has aided inventory management are:
- 10% is the average cost reduction achieved by implementing new technologies.
- 37% of businesses use digital technologies to track their inventory levels meticulously.
- 88% of retailers plan to upgrade their inventory management technology.
Related services and industries
Inventory Management Software
Take inventory control, optimize your supply chain, and achieve sustainable growth.
Streamline Inventory Management With CodeIt