Cloud-Based Inventory Management


A cloud-based inventory management system (IMS) is a solution run on remote servers. All the functionality can be accessed from any location over the Internet. Inventory data is stored and processed virtually by cloud servers.
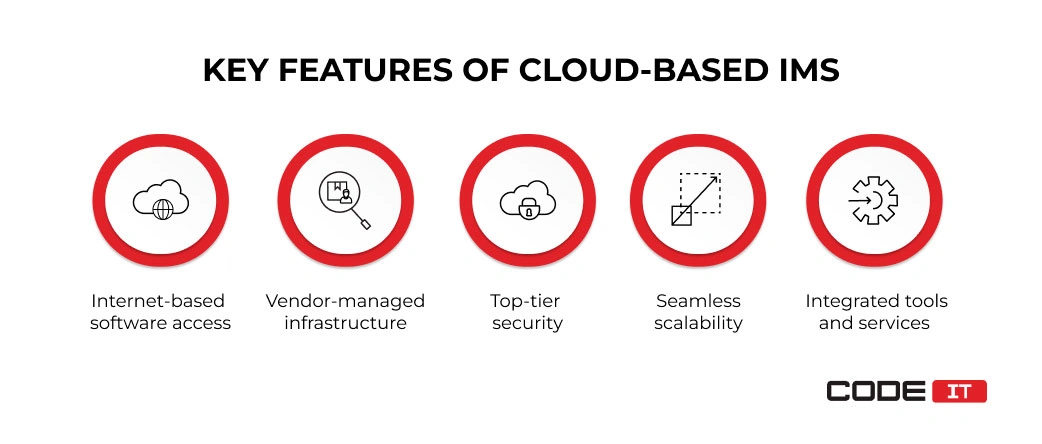
The top three peculiarities of cloud-based inventory management software are:
- Real-time inventory tracking. IMS ensures up-to-date stock information, reducing errors and optimizing inventory flow.
- Access over the Internet. IMS is installed on remote servers and can be accessed by using any device at any location. Software installation may not be required if an IMS is accessed via a web browser.
- Vendor-managed infrastructure. A third-party provider fully maintains remote servers and hardware.
- Top-tier security. A cloud-based infrastructure provides a high level of security. Also, data can be easily recovered in case of unforeseen disaster.
- Seamless scalability. No additional hardware should be installed to increase the computing power and storage capacity.
- Integrated tools and services. Cloud computing providers provide access to integrated tools that help optimize inventory management KPIs, reporting, and data analysis.
In this article, you will learn about the key peculiarities of cloud-based inventory management, positive outcomes, and how to create a new IMS designed to solve unique business problems.
Build a cloud-based inventory management system with CodeIT

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
Cloud-based vs on-premises solution
To fully understand the strengths of a cloud-based IMS, let’s compare its key features with those of an on-premises solution.
| Cloud-Based IMS | On-Premises IMS | |
|---|---|---|
| Installation and Setup | Fast and easy remote server configuration. No hardware should be installed. | Software and hardware should be installed physically. Also, it’s required to establish a network. |
| Accessibility | Stable and secured Internet access is required. | Accessible within a configured network. It can work offline. |
| Maintenance | Remote servers are fully maintained by a vendor. | The entire infrastructure should be maintained by an in-house team. |
| Scalability | Infrastructure can be easily scaled up and down by submitting requests over the Internet. | New hardware should be installed to increase the storage or computing power. |
| Costs | Subscription-based model. Pay only for the resources used. | High upfront infrastructure installation costs. An in-house team of systems administrators is required to maintain an infrastructure. |
| Data Security | Robust data security. Automated backup creation and disaster recovery tools. | In-house specialists manage security and data backup. |
| Hardware Control | 100% of the hardware is maintained and updated by a vendor. | Full control over on-premises infrastructure. |
Benefits of cloud-based IMS
Let’s explore the positive business outcomes and technical benefits of implementing a cloud-based inventory management system.
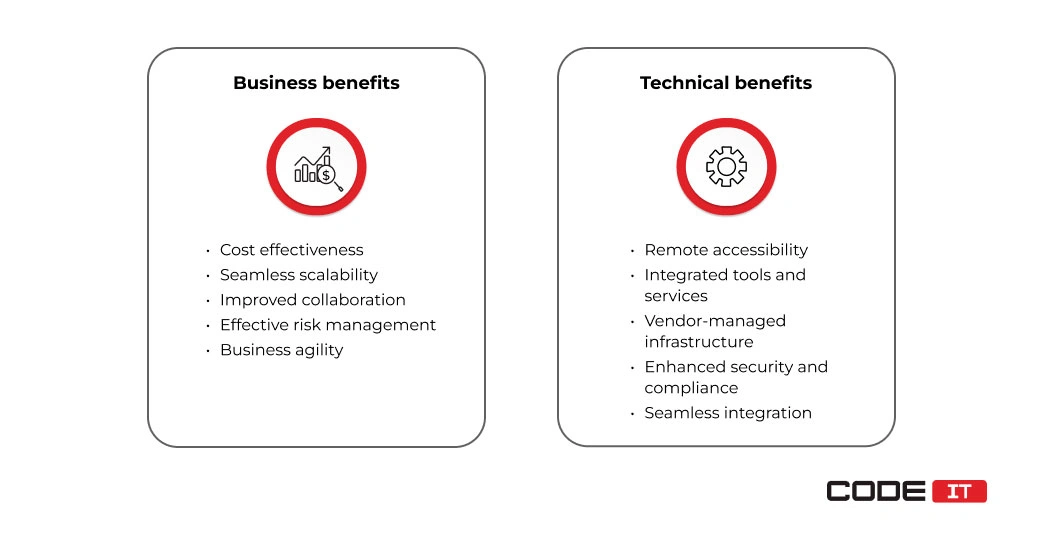
Business Benefits
Business benefits describe the improved financial and risk management outcomes of using a cloud-based inventory system.
- Cost-effectiveness. No upfront installation costs. Moreover, businesses need to pay only for the cloud computing services they use, making it ideal for pricing tiers based on usage.
- Seamless scalability. The computing power and storage capacity can be easily scaled up and down in accordance with business needs.
- Demand planning and forecasting. Advanced analytics tools help businesses predict future inventory needs, reducing overstocking and shortages.
- Improved collaboration. The ability to access inventory management software over the Internet enables the opportunity to create an effective collaborative environment, inlocking automated order and shipping management.
- Effective risk management. Minimized system failure because of top-tier security. Also, cloud providers offer access to automatic data backup and disaster recovery tools.
- Inventory management for multiple locations. Businesses with warehouses, retail stores, and distribution centers in different regions can manage stock across various locations efficiently.
- Business agility. Fast system scalability and a large variety of integrated tools help rapidly respond to ever-changing business environments.
Technical Benefits
Technical benefits refer to optimized operations and technical solutions of cloud-based inventory management software.
- Remote accessibility. Dedicated servers can be managed remotely. Also, the cloud-based IMS can be accessed from any device over the Internet.
- Integrated tools and services. Top cloud computing services providers enable access to advanced integrated solutions. They can be applied to improve workflows, analyze data, manage IoT devices, etc.
- Vendor-managed infrastructure. Remote servers are 100% managed and maintained by a third-party company.
- Enhanced security and compliance. Cloud-based infrastructure enables top-tier security and data protection. Also, it provides the opportunity to better comply with regulatory requirements.
- Seamless integration. Cloud-based inventory management software is easy to integrate with third-party software.
Want to switch to a cloud-based IMS?

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
Use cases of cloud inventory management
Cloud-based infrastructure helps businesses unlock growth opportunities and optimize processes. The foremost applications of cloud IMS are as follows.
Real-Time Tracking
The ability to collect real-time data from multiple sources in a centralized repository enables organizations to track the movement of items in real time. Moreover, cloud-based infrastructure ensures maximum uptime to always have instant access to real-time inventory visibility, stock levels, movement, and location data from any device.
Demand Planning and Forecasting
The usage of AI in fulfillment processes and raw data analysis provides organizations with insights into their inventory operations. The technology’s ability to detect trends, repeating patterns, and non-linear data correlations helps forecast demand in the future. As a consequence, businesses manage to create well-thought-out stock replenishment plans, minimizing losses and expenses while optimizing inventory turnover. Additionally, businesses can leverage advanced reporting to analyze performance metrics and identify supply chain problem reduction opportunities.
Multi-Location Inventory Management
Centralized data collection helps implement multi-channel listing and inventory management. Using a single digital tool, businesses can get a comprehensive overview of inventory tracking software across different locations in real time. In addition, businesses can implement helpful features like cross-location stock transfer requests to manage all operations effectively, ensuring traceability of stock movements.
Automated Stock Replenishment
The ability to monitor inventory levels in real time across multiple locations helps create automated stock replenishment. Cloud servers help connect various systems from diverse vendors for real-time information exchange and functionality sharing. Seamlessly connect with suppliers, ERP systems, and e-commerce integrations via APIs to automate stock replenishment operations. Also, cross-system data sharing is helpful for enabling vendor-managed inventory and facilitating partial shipping and invoicing.
Equipment Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
Continuous equipment data collection via an IoT network and analysis helps monitor changes in equipment operations. AI-driven tools used for predictive maintenance can detect minor changes in vibration, noise, temperature, and other factors, forecasting when a piece of equipment is likely to fail. This helps businesses extend the lifespan of equipment by fixing technical issues in the early stages. Also, they order the required replacement parts in advance and plan maintenance activities to minimize downtime.
Custom cloud-based IMS development guide
The cloud-based inventory management software development process comprises six key stages.
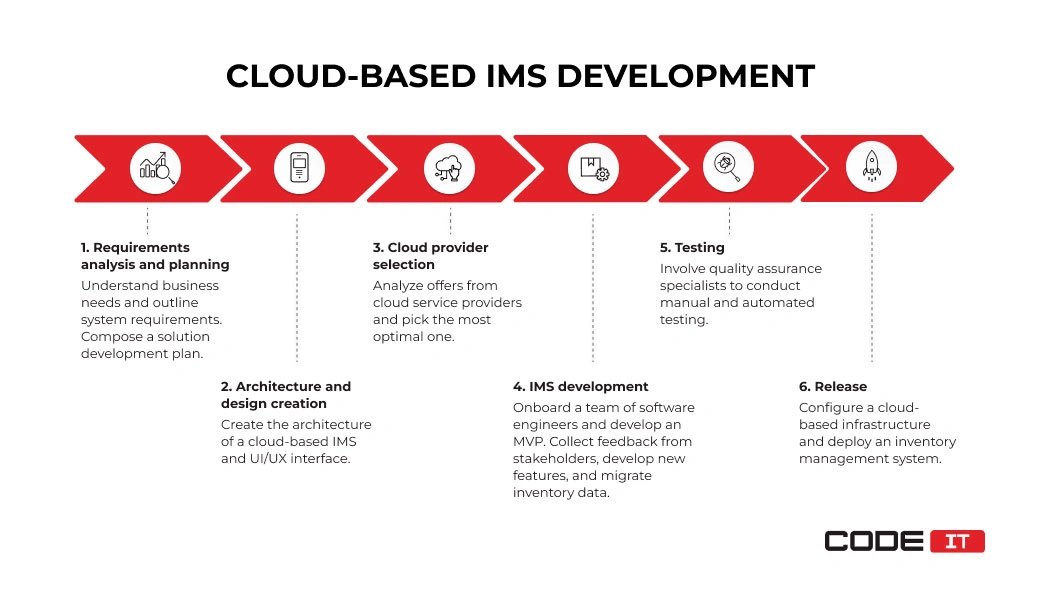
1. Requirements Analysis and Planning
Analyze the specific needs of your business. Understand the main challenges of inventory management and if they can be solved by switching to a cloud. Also, it’s required to form a business vision and long-term development plan.
Outline requirements for a new inventory management system, including CRM integration, POS integration, and eCommerce integration if needed. Compose functional and non-functional requirements. Consider customizable software features to align with business needs.
Compose a software development plan. It should imply a backlog of tasks, user stories, the “definition of done” for features, and responsible roles.
| Output artifacts | Involved roles |
|---|---|
| Software requirements specification | Business analysts |
| Solution development plan | Stakeholders |
2. Architecture and Design Creation
Develop the architecture of a cloud-based inventory management system. Choose the most optimal technology stack. Define a set of features that should be implemented, including native integrations, and third-party systems to connect with your IMS.
Create the UI/UX interface of a new IMS. It should imply wireframes that outline interface components and placement.
| Output artifacts | Involved roles |
|---|---|
| IMS architecture | System architect |
| Tech stack | Designer |
| System design | Project manager |
| Wireframes |
3. Cloud Provider Selection
Select a cloud service provider. Analyze the top services offered, prices, scalability options, integrated features, etc. The top three cloud service providers are:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Google Cloud
- Microsoft Azure
| Output artifacts | Involved roles |
|---|---|
| Cloud platform comparison report | System architect |
| Best provider reasoning report | Software engineers |
4. IMS Development
Onboard a team of software engineers and share all the documentation. The involved specialists should:
- develop a prototype and collect feedback
- create the MVP of an inventory management system
- refine the developed product by releasing new features incrementally
- test the product and fix detected bugs
- deploy the inventory management system on a cloud server
- prepare technical documentation and user guides
Additionally, software engineers may be required to:
- connect the IMS with other services and tools used by a company
- migrate inventory data from a previous IMS
- implement scanning and barcoding for improved traceability and asset management
| Output artifacts | Involved roles |
|---|---|
| Prototype | Software engineers |
| MVP | Database administrators |
| IMS deployed on a cloud server | System administrators |
| Technical documentation | Project manager |
| Technical writer |
Inventory Management System Features
5. Testing
Onboard quality assurance (QA) engineers. They need to conduct manual and automated software testing. Detected bugs should be documented. Software engineers are responsible for fixing identified bugs, security issues, and other problems while ensuring smooth warehouse management.
| Output artifacts | Involved roles |
|---|---|
| Bug and test reports | QA specialists |
| Stakeholder feedback | Project manager |
| Stakeholders |
6. Deployment
Configure a remote server and release the cloud-based inventory management solution. Test the application in a real-world environment and maintain the cloud infrastructure to ensure the maximum IMS uptime with proper account configuration.
| Output artifacts | Involved roles |
|---|---|
| Configured cloud-based server | Software engineers |
| Deployed cloud-based inventory management software | System administrators |
| Project manager |
Codeit case study — ConnectSx
The CodeIT team has developed an innovative cloud-based hospital inventory management system. It works in web browsers and mobile devices.
Problem
The client wasn’t satisfied with the functionality of the existing inventory management system. Our team was hired to optimize the system and implement new industry-specific inventory management features.
Solution
Our team has thoroughly analyzed the existing solution. Our tech specialists have conducted a technical audit. We’ve prepared a detailed project reboot plan to implement a new cloud-based inventory management software that is fully aligned with the client’s business needs.
Following the approved plan, we developed a new inventory management, implementing all the requested features. The solution is tailored for managing medical products and inventory. The three apps created by the CodeIT team include:
- Web app
- Mobile app
- Mobile barcode scanning app
Want to learn more about CodeIT’s input to the cloud-based inventory management system development project? Read the detailed case study.
Summing up
Cloud-based inventory management software is installed on a third-party company’s remote servers. The five key characteristics of a cloud-based IMS are:
- Real-time inventory tracking
- Access via the Internet
- Vendor-managed infrastructure
- Seamless scalability
- Integrated tools and services
The usage of cloud-based IMS helps businesses spend money efficiently and eliminate upfront infrastructure installation costs. Also, it enables seamless system scalability, hassle-free server management, and software access from any location over the Internet.
Let’s discuss your inventory management needs

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
FAQ
The term cloud-based IMS defines software that is installed on remote servers. It can be accessed via the Internet from any location and device. Inventory data is stored on remote servers as well. A third-party vendor fully manages cloud-based servers.
The key peculiarities of cloud-based inventory management software are:
- Access via the Internet
- Server is maintained by a vendor
- Top-notch security and automated data backup
- Easy to scale up/down
- Integrated tools and services
The benefits of switching to using a cloud-based solution for managing inventory include the following:
- Remote accessibility
- Integrated tools and services
- Vendor-managed infrastructure
- Enhanced security and compliance
- Seamless integration
The business benefits of using cloud servers include:
- Cost-effectiveness
- Seamless scalability
- Improved collaboration
- Effective risk management
- Business agility
The six steps of building a new cloud-based inventory management system from scratch are:
- Requirements analysis
- Planning and design
- Cloud provider selection
- Inventory management system development
- Testing
- Deployment
Build your ideal
software today