IoT In Warehouse Management — Extensive Guide


The Internet of Things (IoT) is a concept of systems developed by connecting a large number of smart devices into a network. IoT-enabled systems help establish innovative warehousing and increase the level of automation. In essence, they help streamline inventory management and reduce operating costs.
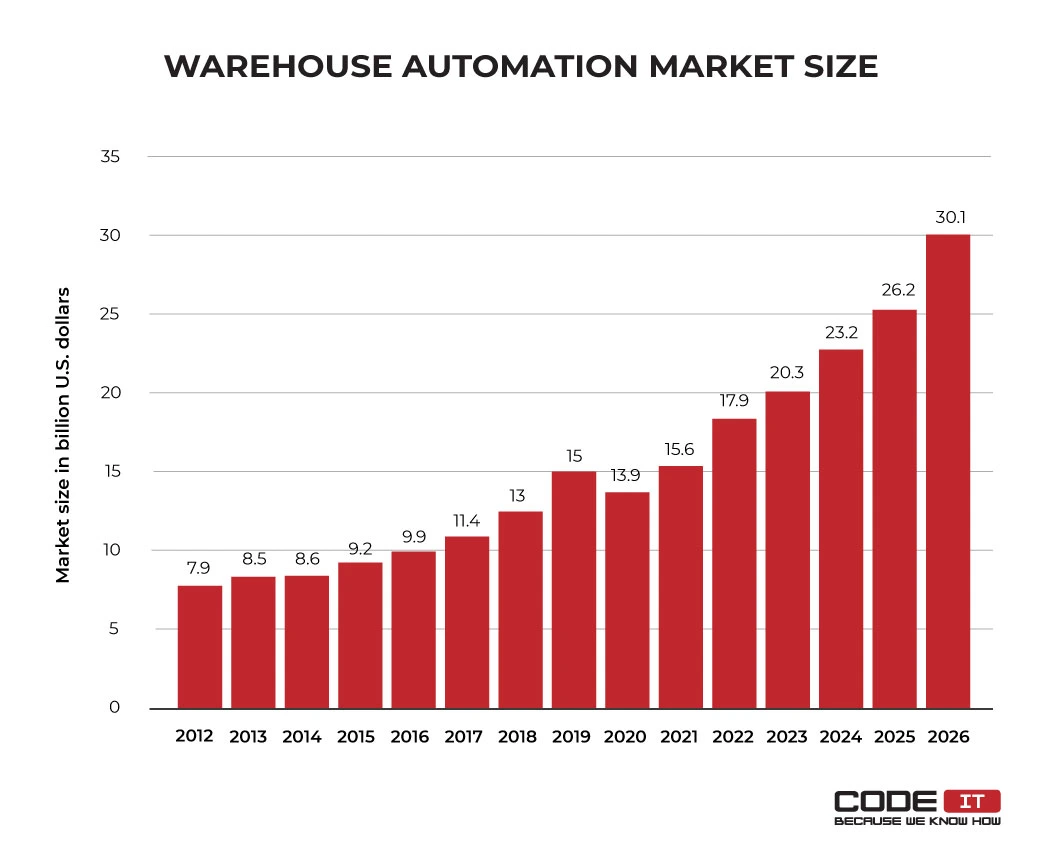
According to recent statistics, technology adoption in warehouse automation is rising rapidly. Moreover, the number of responders who will adopt IoT in warehouse management will double by 2030.
How IoT Warehousing Works
The use of intelligent devices connected to one system promotes the fourth industrial revolution development.
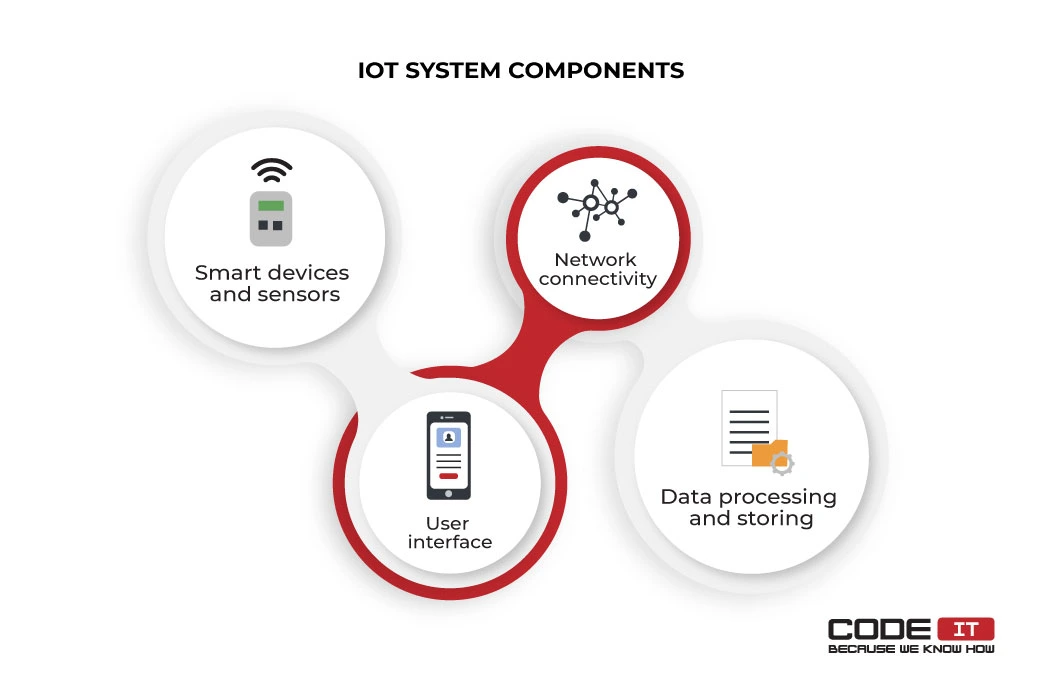
The four core components of an IoT system are:
- Smart devices and sensors — IoT devices are the essential component of an intelligent warehouse. Smart sensors and IoT devices gather data and send it to processing units.
- Network connectivity — Wired or wireless networks are used to connect IoT devices into one system. Network connectivity helps transfer all the data acquired by IoT devices to a server.
- Data processing and storing — A processing unit or server that is used to analyze all the data received. Also, it can store data for further usage.
- User interface — An application that helps users access raw data or get useful insights. Usually, the layer has the form of a dashboard that conveniently displays the required information. Also, the user interface should offer the opportunity to send commands to establish centralized IoT warehouse management.
An IoT system foresees the opportunity to gather data automatically and send requests to intelligent devices. The architecture of an IoT-enabled warehouse management system is the following:
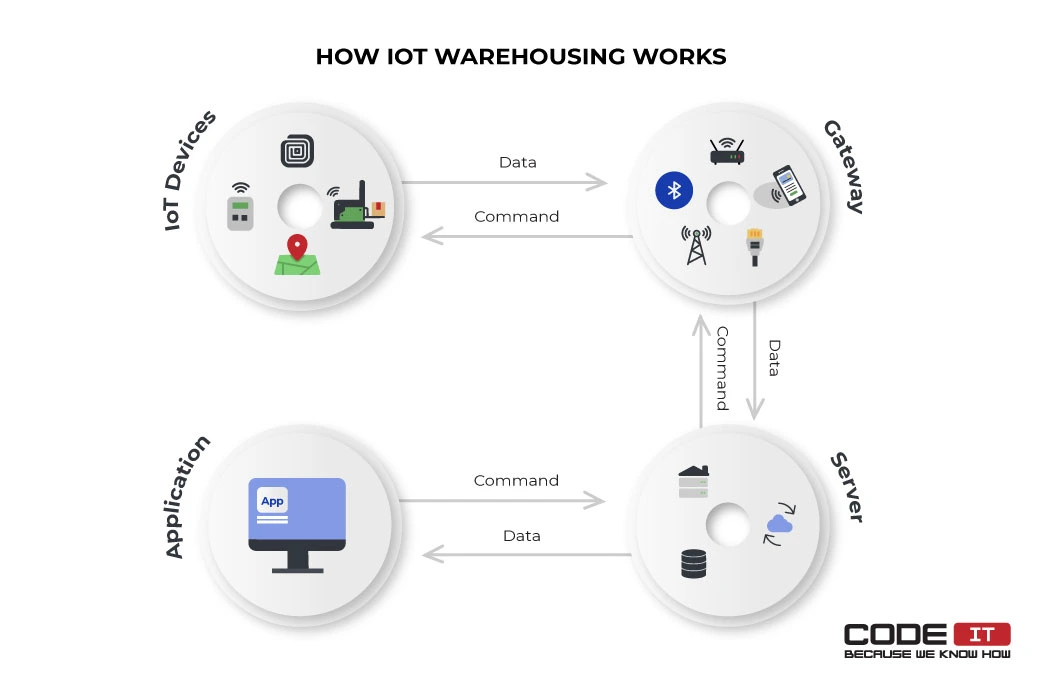
1. IoT Devices
All types of smart sensors and IoT devices gather raw data, so it get processed by IoT-based systems. Usually, intelligent devices track the placement of assets and help monitor warehouse environments. Also, they help track the number of items left in a warehouse and new packages that arrive at a warehouse.
2. Gateway
A gateway connects IoT warehouse devices to the Internet or local network to establish an IoT in warehouse management system. Smart devices can be connected via:
- WiFi network
- Ethernet connection
- Bluetooth connection
- Cellular network
- Near Field Communication (NFC)
3. Server
A dedicated computer receives raw data from IoT devices. All the data is processed to get valuable insights or saved for further usage. In order to automate the warehouse management process, a server can send commands to smart devices following developed algorithms.
The two types of servers that can be used are:
- Cloud-based — A dedicated or shared server installed and maintained by a third-party company. It offers the opportunity to scale the disc space and computing performance upon demand. Access to a cloud server is provided via the Internet.
- On-premises — A physical server installed in a warehouse to create a local network of IoT devices. An on-premises server uses physical hard drives to store data and has limited computing power.
Let’s compare the two types of servers in more detail.
| Cloud-based | On-premises | |
|---|---|---|
| Data control | All the data is transferred to a cloud server via the Internet. | All the information is transferred to an on-premises server using a local network or Internet connection. |
| Scalability | It can be easily scaled up upon demand manually or automatically. An external vendor provides additional computing power. | Additional hardware needs to be installed for vertical scaling. |
| Launch time | Fast and stress-free launch. | A business needs to purchase the required hardware and install it. |
| Cost | A business needs to cover the subscription fee only. It depends on the amount of computing power assigned. | A business needs to cover the following expenses: installation, maintenance, scalability, security, storage, and downtime losses. |
| Maintenance | Maintenance is provided by a vendor. | It’s required to have dedicated specialists for on-premises server maintenance. |
| Security | High level of security. However, data is transferred via the Internet. | A company fully manages security. There is an option to build a local network. |
| Hardware control | All hardware is chosen and managed by an external vendor. | A company is responsible for installing and updating hardware. |
Need expert advice?
We’re ready to help!

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
4. Application
A mobile or desktop application with a well-thought-out user interface offers the opportunity to consume information and send commands. An application should be integrated into an inventory management system to track all the items in a warehouse.
The IoT-driven warehouse system has a two-way connection. Hence, a user or server can send commands to IoT devices using a gateway.
5. Edge Computing — Additional Layer
Large warehouses with rich IoT systems use an additional layer. The edge computing layer is located between the gateway and data storage layers.
It implies extra edge nodes that can analyze data from smart devices and issue commands without sending information to the central server.
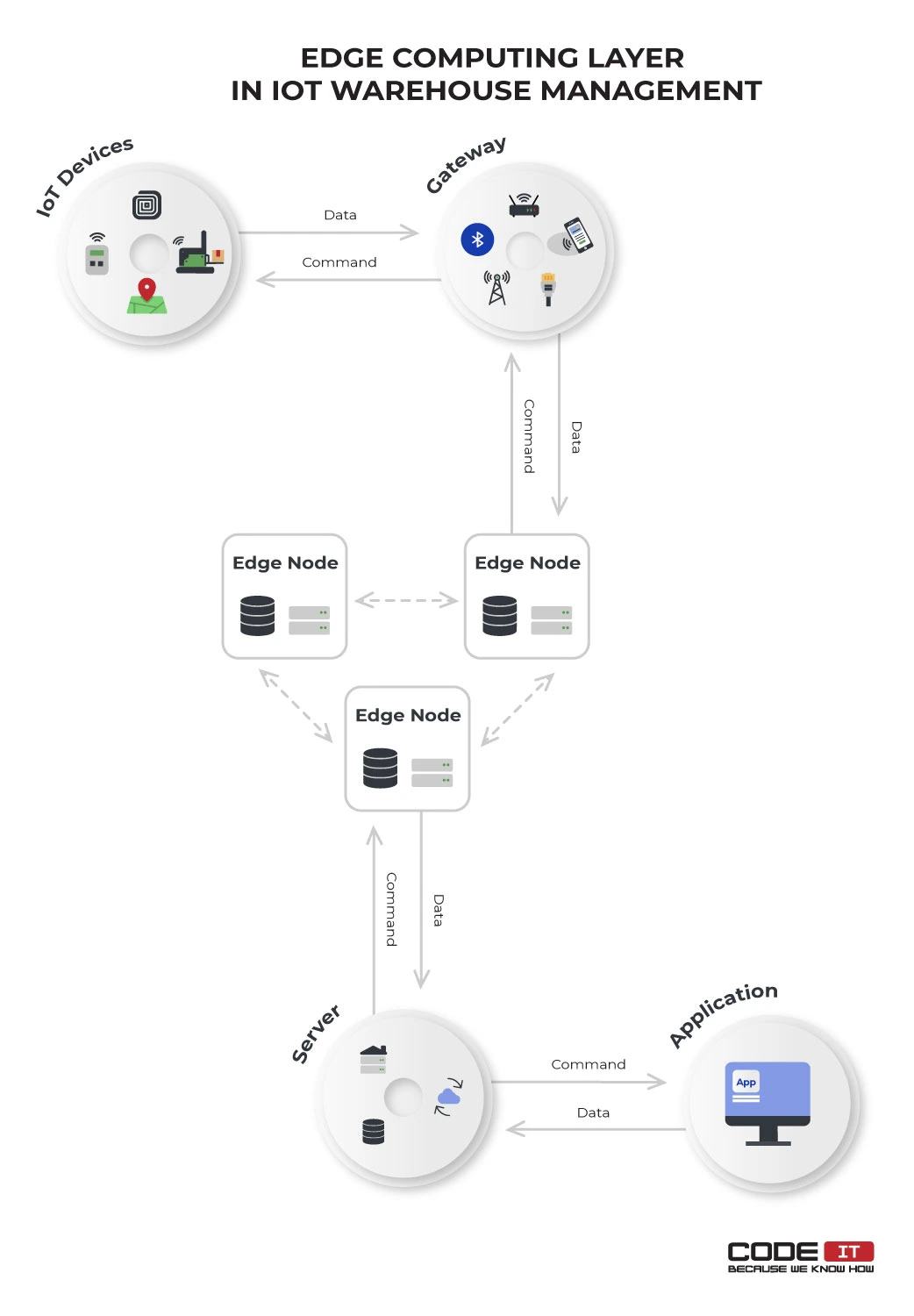
The benefits of adding the edge computing layer are the following:
Improved speed
Usually, data processing units are installed near IoT devices and are designed to analyze data acquired from specific sensors only.
Consequently, it improves the speed of data processing and command issuing, which is vital for real-time tracking and sensors that help monitor safety. The quick response time is crucial for fire alarms, collision detectors, or gas leak prevention actuators.
Lower amount of data transferred
Large systems that utilize the Internet of Things in warehouse management and large-scale warehouse IoT solutions must transfer enormous amounts of data to the central server. Consequently, it increases the load on the gateway layer.
The integration of edge processing helps minimize the amount of data transferred to the central server.
Reduced amount of data processed by the main server
The increased amount of data that needs to be analyzed affects the required computing power, which causes additional expenses. In the case when units in the edge computing layer process most data, the main server receives the minimum amount of information.
In essence, a lower amount of computing power is required. It causes decreased cloud server bills or cheaper maintenance of on-premises servers.
Optimized data storage
A large amount of disk space is required when transferring all the data from IoT devices to the central server. However, the edge computing layer can optimize the amount of data needed to be stored.
Additional computing units can analyze large amounts of raw data from smart devices and sensors to form valuable insights. They transmit the insights or condensed data to the main server.
The optimized amount of data needed to be stored reduces the demand for free disc space.
Enhanced scalability
One of the core advantages of the edge computing layer is the ability to scale up the use of IoT in warehouse management for seamless administration of supply chains.
The load on the central server and network does not increase significantly when new devices are added. Consequently, businesses can quickly scale up their warehouses by adding many new intelligent devices, smart sensors, and additional data processing units to the system.
Iot Devices and Use Cases
The is a large assortment of smart devices used for building smart warehouses. The most popular types of IoT devices are:
RFID Tags
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags are the most widespread technologies used in inventory management. Every tag is unique and holds information about a product. A tag can transmit data using radio waves.
An RFID tag can hold many types of information. The most common data types are:
- Tag’s serial number
- SKU number
- Name
- Location
- Weight
- Production date
There are two types of RFID tags:
- Active — A tag can access an energy source to generate radio waves transmitting data. Active RFID tags include an integrated circuit, antenna, battery, and an onboard transmitter. This type of tag has a more extended range.
- Passive — Radio waves transmitted by an antenna generate current in an RFID tag so that it can share data. Passive tags have a short range. They consist of two parts: an integrated circuit and an antenna.
The core advantages of this technology are:
- Fast scanning — The technology foresees the opportunity to scan RFID tags in bulk. A scanner can read hundreds of tags at once. Therefore, the technology is beneficial for high-load warehouses.
- No light requirements — RFID tags transmit data using radio waves. Therefore, there is no need to pour light on a tag to scan it.
- Ability to read and write data — Most types of RFID tags offer the opportunity to read and write data. Consequently, information can be updated, and tags can be reused. The serial number of tags is the only data type that cannot be updated.
- Durable design — RFID tags can be used in harsh environments and last long.
- Option to encrypt data — The technology offers the opportunity to write encrypted data to tags to enhance the security of inventory management.
- Barcode system integration — Barcodes can be printed on RFID tags to integrate them with barcode scanning systems.
Develop an IMS with custom features

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
Beacons
Beacons are small Bluetooth-powered devices that help facilitate inventory management. They come in different sizes and shapes. Besides, they may have various technical specifications.
A beacon has an in-built battery to maintain continuous Bluetooth connectivity. Beacon tags can help track the location of assets precisely, which is the primary aim of the technology. Meanwhile, they can also contain data about products they are attached to.
In order to share information about an item’s location and properties, beacons need to be connected to another device via Bluetooth. A connected device becomes a point of network for a beacon when connected.
Here is how beacons work in more detail:
- A beacon device emits a Bluetooth signal
- The Bluetooth signal is picked by a device connected to a network
- Data is transferred from a beacon to a server for further processing
The key points to know about using beacons for IoT in a warehouse are:
- Bluetooth signal is emitted constantly — Any device can pick it simultaneously when reaching the required range. It facilitates live-time tracking of items in a warehouse.
- Data storage option — Beacons can hold from 60 to 450 bytes of data.
- Precise indoor positioning — Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology helps detect the distance to an asset indoors if one device is connected. If several devices are in a beacon’s Bluetooth range, the technology can also determine the direction for precise positioning. The feature offers a competitive advantage over GPS trackers.
- Extensive range — Unlike Near Field Communication (NFC) technology, beacons can emit Bluetooth signals that have up to a 230-feet range.
- Option to install additional sensors — Beacons offer the opportunity to install additional sensors for measuring the temperature, light level, humidity, movements, etc.
- Long-lasting battery life — Since beacons use the BLE technology, they can work from 18 to 24 months on one battery. The battery life depends on the number of extra features. Beacons can work from 6 to 8 months in case additional sensors are installed. Energy-saving models of beacons can work for up to 5 years without the need to replace a battery.
Beacons can be attached to:
- Assets — The most widespread use of beacons. They help monitor items in a warehouse and locate them fast.
- Vehicles — With the help of additional sensors installed, beacons can help monitor the location of cars, performance, idle time, etc. Also, they can notify about collision risks.
- Tools — Help track tools used in a warehouse and help identify their location fast.
- Workers — Wearable beacons can track workers’ performance and identify idle time.
Smart Sensors
An IoT warehouse can be easily managed and maintained from one place if intelligent sensors are installed, and modern warehousing techniques are applied.
Smart sensors have inbuilt processing units that help detect certain items and analyze data collected before transferring it using a network connection. Moreover, they can help automate a lot of processes and enhance security.
The types of smart sensors used for IoT warehouse management are the following:
- Acoustic — Detect audio vibrations to define dangerous environments for workers and meet local regulations.
- Chemical — Analyze the composition of fluids stored in a warehouse to detect dangerous cargo or meet quality standards.
- Electrical — Measure the voltage, current, and power in a grid to help keep the electrical network of a warehouse safe.
- Environmental — Monitor physical conditions in a warehouse. Environmental sensors can detect and measure temperature, gas leaks, humidity, air pressure, light, etc.
- Image — Capture video using a camera, infrared, or ultraviolet (UV) sensors. Most smart image sensors can detect motion. Usually, image sensors are installed for security purposes.
- Motion and force — Smart sensors that measure motion, weight, size, vibration level, position, rotational, etc. Motion and force sensors facilitate inventory management by tracking assets and their properties automatically.
- Touch — Detect physical contact with an object. Tech sensors can measure the pressure applied or utilize the human body’s natural conductivity to detect touches.
The most widespread smart sensors on the IoT in the warehouse management market are temperature and humidity sensors. They help maintain the required conditions to store items properly. In case any unacceptable environmental conditions are detected, managers get notified immediately.
GPS Trackers
GPS trackers are widely used in fleet management. Smart trackers can help facilitate warehouse assets, tools, and vehicle tracking. For instance, GPS trackers can be attached to palettes, storage racks, forklifts, and other devices for precise positioning.
Unfortunately, low signal and accuracy make GPS trackers less reliable indoors. However, they work accurately outdoors. Therefore, if assets are stored on large outdoor sites, GPS trackers can help find the required items fast.
The smart features of GPS trackers help enhance the application of IoT in warehouse management. The core features of smart GPS trackers are:
- Live time tracking — Being connected to the Internet, GPS positioning data is sent to a server for live time traceability.
- Geofencing — Users can set operating and storing zones for assets, tools, and vehicles. In case any tracking items leave the permitted working zone or get misplaced, a manager gets a notification simultaneously.
AI Cameras
The use of cameras in an IoT warehouse isn’t limited to security as the main role of technology in warehousing. AI-powered cameras use artificial intelligence to monitor all the processes. They are capable of identifying objects captured by using smart algorithms. Also, they can define patterns and notify managers about accidents.
The main advantages that drive businesses to start using smart cameras when adopting the Internet of Things in a warehouse are:
- Easy installation — Smart cameras can be connected to a network using WiFi or Ethernet. Also, they may have in-built batteries. Wireless devices are easy to install in various locations. Nevertheless, a wired power connection is the most popular option because it erases the need to replace batteries.
- Object identification — Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) offer the opportunity to identify objects and their properties. For instance, a camera can count the number of storage racks or boxes passed by to control all items in a warehouse meticulously.
- Remote access to cameras — With the help of an Internet connection, cameras can broadcast captured video in live time. Consequently, managers can use applications to access the video from any location to monitor all the processes.
- Motion detection — Video captured in high resolution may require a lot of storage space. In order to minimize expense, smart cameras have in-built motion-detection sensors, so they film when objects move within their focus distance.
Machine Learning in Supply Chain
Smart HVAC Systems
Smart heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems help streamline the usage of IoT in warehouses. Automation helps minimize expenses and keep the required environment in a warehouse stress-free.
In most cases, intelligent HVAC systems have the form of detectors and accelerators connected into one system to maintain the optimal environments automatically.
For instance, a smart thermostat measures the temperature and sends commands to keep the required condition. Also, the application of the Internet of Things in warehouses can help build HVAC systems run by certain algorithms.
The use of smart HVAC systems for IoT in warehouse management and maintenance helps achieve the following:
- Reduced utility bills
- Optimized energy system load
- Automatic maintenance
Also, smart HVAC systems have beneficial advantages that are:
- Predictive maintenance
- Real-time alerts and monitoring
- Detailed analytics
- Guaranteed regulatory compliance
IoT Warehousing Trends
The Internet of things in the warehouse management market keeps rising at a high pace. Many companies develop new devices that help leverage the power of technologies to enhance warehouse management.
The top three technologies used to streamline the IoT in warehouse management and inventory tracking are:
AR Glasses
The use of smart glasses is an upcoming trend in IoT warehouse management. Augmented reality (AR) glasses can add additional content to lenses, facilitating the work of personnel.
For instance, AR glasses can show workers a list of items they need to pick and directions.
The top features of AR glasses that help boost the performance of workers are:
- Speech recognition — It allows sending commands by voice and communicating with others hands-free.
- Barcode scanning — In-built barcode scanner erases the need to use external devices. Workers can quickly scan barcodes of items by pointing glasses at them. Information about items can be shown on lenses or sent to a server via a gateway.
- Replaceable batteries — Smart glasses consume a lot of energy, so they need a reliable energy source. Replaceable batteries can provide the full-shift working capability for AR glasses.
- Video capturing and streaming — Some devices have in-built cameras to capture all the activities on video. Moreover, this IoT warehouse device can help stream video in live time and hands-free.
Automated Guided Vehicles
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are small robots that help adopt the autonomous inventory management approach. AGVs are small robots that move assets in a warehouse automatically. They navigate in an IoT warehouse using floor stickers, LiFi technology, vision cameras, or wires.
The core advantages of this technology are:
- Automated assets moving
- 24/7 work
- Great performance in monotonous tasks
- Automated route picking
- Automated charing
- Reduced risk of human error
- Easy to scale up by adding new AGVs
These days, many enterprise-grade companies use automated guided vehicles to enhance IoT in warehouse management and increase automation.
Drones
Drones can facilitate inventory tracking in an IoT warehouse. They can operate indoors and outdoors without any issues. Drones that float indoors have protection cases installed to keep blades safe in case of a collision.
With the help of drones, workers can easily make large distances and explore the upper shelves of a rack without the need to use a ladder. They can find the required items and scan codes remotely. Also, drones can be used to examine the condition of other tools and constructions without reaching them physically.
Some advanced drone models can be used to transport packages in a warehouse.
Warehouse Automation System — Top Solutions and Trends
Application Of IoT In Warehouse Management
There are many other ways businesses adopt IoT in warehouse management because of the large assortment of smart devices and the ability to connect them to a system.
Let’s check the most widespread examples of IoT in warehouse applications for inventory management and monitoring.
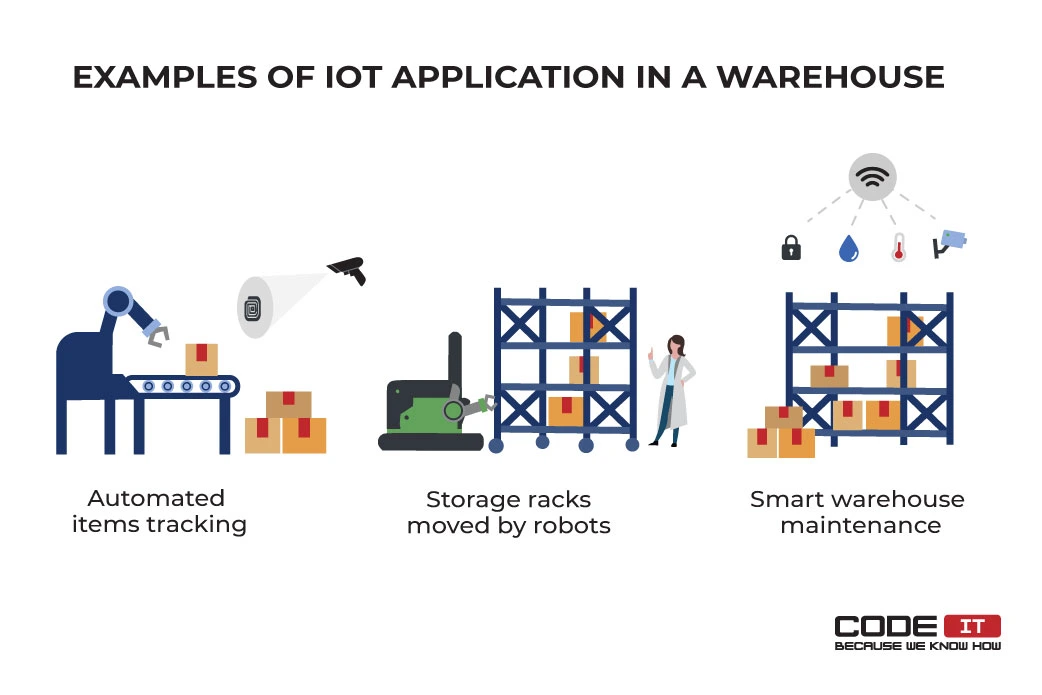
Automated Items Tracking
Developing IoT in warehouse management is tough without thorough tracking of items. Automated item tracking helps track every item entering or leaving a facility. An inventory management system must know all the details about objects, their current location, and storage places.
Automated items tracking has the form of devices that detect codes, scan them, and send information about assets to a server.
For instance, automated item tracking can be adopted in an IoT warehouse with the help of devices that scan barcodes or signs on racks moved by AGVs. Also, an RFID tag scanner can be installed on a belt to track all items that pass by.
Storage Racks Moved By Robots
Automated guided vehicles that move storage racks are one of the most widespread types of IoT in warehouse management. Robots can take shelves with items to the picking and packing zone automatically.
After picking up the required products by workers, AGVs move shelves to the defined storage place in a warehouse. Robots can also automatically take empty shelves to the putaway zone and move them to the storage zone. Hence, workers can store incoming products without the need to move into a warehouse.
Amazon is one of the youngest adopters of this technology. The company has been using automated guided vehicles to move assets in its warehouses for over ten years.
Smart Warehouse Maintenance
The application of the Internet of Things in warehouses helps make the maintenance process less burdening. Smart warehouse maintenance requires businesses to install many sensors, actuators, and HVAC systems connected to the Internet.
For example, an average smart warehouse needs to imply thermostat and humidity sensors that are connected to one system. Smart sensors track the environment in a warehouse and send commands to HVAC systems to maintain the required conditions.
Businesses can easily scale up IoT in warehouse management by installing various sensors and actuators like smart locks, gas leakage sensors, or smart bulbs.
CodeIt IoT Warehousing Expertise
The CodeIT team has rich experience in building IoT-integrated tools for centralized monitoring and control.
The most recent solutions we delivered to our clients have been developed by the CodeIT AI Lab—to streamline warehouse management using the latest tech.
Learn more about the tools we’ve created and problems solved for our clients below.
1. AI-Driven Maintenance
The tool is fully integrated with the client’s IoT devices. It collects all the data and analyzes it using AI, delivering real-time insights and predictive maintenance recommendations. Also, it comprises a smart assistant for the tech team.
Problem
The client experienced unplanned downtime and high maintenance costs. The problems were caused by the extensive labor involvement and poorly planned maintenance schedules.
Solution
The software development process is composed of analysis, planning, and development (MVP + new features each sprint). Also, our specialists created custom integrations with the client’s IoT sensors and prepared technical documentation.
The core components of the AI-driven predictive maintenance solution are:
- Real-time data. All the data is collected from the IoT sensors installed in a warehouse and is transferred to the central server.
- Self-hosted architecture. The AI tool is installed on on-site services—no information is shared with third parties.
- Failure prediction. A machine learning (ML) model was trained on the client’s data. It helps predict when certain equipment is likely to fail and analyzes the root causes, using the collected data.
- Automated maintenance scheduling. The integration with the client’s maintenance planning workflow enabled the creation of the smart planning feature. Technicians automatically receive instructions and alerts thanks to the computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) interface integration.
- Dashboard & real-time alerts. All data about warehouse operations can be accessed conveniently on various devices through a custom dashboard.
AI technician assistant. The tech team is supported by an AI agent that is trained on the internal knowledge base and an extensive number of manuals.
2. Computer Vision and Control
The “digital eye” that comprises an IoT-integrated AI vision system helps automatically monitor warehouse operations, responding quickly to unforeseen challenges.
Problem
Manual warehouse inspections are prone to inefficiencies, with key problems frequently going unnoticed.
Solution
The CodeIT team developed a custom machine learning (ML) model and trained it using the warehouse operations photos provided by the client. The solution was deployed gradually with fine-tuning sessions, improving the performance.
The key components of the AI vision and warehouse inspection system are:
- IoT integration. Data from smart cameras and sensors is gathered on the central server in real time, enabling centralized operations monitoring.
- AI vision. Images are processed in milliseconds, detecting anomalies in a warehouse, equipment failure, improper item placement, etc.
Benefits Of Applying Iot In Warehouse Management
The adoption of IoT positively impacts warehouse management because of automation evolvement.
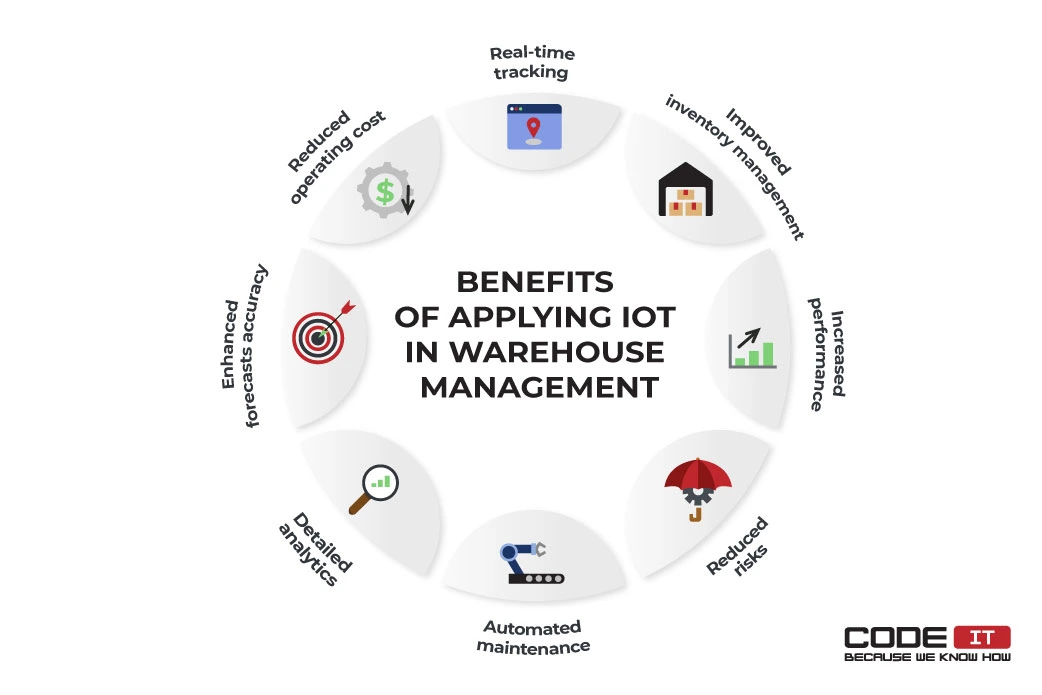
Reduced Operating Costs
Inventory and warehouse management automation provided by IoT devices helps minimize operating and labor costs. Also, intelligent devices help increase performance and deliver valuable insights to reduce expenses on warehouse management.
Real-Time Tracking
IoT devices offer the opportunity to track all the assets in real time. Managers can easily access live-time data and send commands that will be performed simultaneously. It streamlines inventory management and helps reduce the risk of failure.
For instance, RFID scanners installed on a belt can scan tags on items and send data to a warehouse management system in live time. Also, it can update the information on RFID tags or write additional details.
Improved Inventory Management
With the help of IoT devices like beacons, businesses can track the precise location of assets. A warehouse management system can suggest the most optimal item storage layouts, having a large amount of data on the item’s location. Consequently, a company will be required to spend fewer resources on the assets moving and delivering them faster.
Increased Performance
Automation helps perform routine tasks fast and without any interruptions. Real-time tracking and data-driven analysis deliver wise suggestions for improving workers’ performance and optimizing warehousing processes.
Enhanced Forecasts Accuracy
IoT devices and intelligent sensors help collect large amounts of data. It can be analyzed to increase the accuracy of demand forecasts. Also, smart devices make the maintenance of a warehouse more transparent so that a business can predict utility expenses more accurately.
Automated Maintenance
IoT devices help reduce the demand in the labor force to maintain a warehouse. Smart sensors can collect information about temperature, humidity, leaks, etc. A server can send commands to adjust HVAC systems or engage actuators automatically, being connected to one system.
Reduced Risks
The wide usage of technologies helps minimize the risk of human error in warehouse management. Smart sensors can notify workers about the excess load on racks or a chance of a forklift collision, keeping a business safe from unforeseen accidents. Also, smart locks, cameras, and motion sensors can minimize the risk of fraud or product theft.
Detailed Analytics
Smart devices help get detailed analytics and helpful insights in one place because they can collect and transmit large amounts of raw data via different networks.
Summing Up
IoT in warehouse management is a new trend in the logistics industry. Using smart technologies united into one system helps facilitate inventory management and automate many processes. Essentially, it helps reduce operational costs, lowers risks, and boosts performance. Faster delivery of goods also helps increase customer satisfaction.
The share of IoT in the warehouse market is rising continuously because smart devices also help fight upcoming challenges in supply chain management. Labor force shortage, overstock, and asset misplacement are the main challenges that the use of IoT in warehouse management helps overcome.
FAQ
It is a concept of building systems that consist of intelligent devices connected to the Internet or a local network. The use of smart sensors, scanners, robots, and other devices helps automate processes and facilitate inventory management.
Using smart devices connected to a network offers the opportunity to enhance inventory management, boost performance, and fight upcoming challenges. Moreover, the adoption of intelligent devices helps get a technological advantage over competitors
There are many technologies used for IoT in warehouse management. The top technologies are:
- RFID Tags
- Beacons
- Smart Sensors
- GPS trackers
- AI Cameras
- Smart HVAC systems
- AR Glasses
- Automated guided vehicles
- Drones
Businesses use smart devices to build IoT systems in warehouse management. For instance, with the help of smart devices, they can establish the following:
- Automated inventory tracking
- Smart warehouse maintenance
- Storage racks moved by robots
The main pros of using IoT in warehouse management are:
- Reduced cost
- Real-time tracking
- Improved inventory management
- Increased performance
- Enhanced forecasts accuracy
- Automated maintenance
- Reduced risks
- Detailed analytics
Amazon is one of the top technology adopters in warehouse management. The company uses many smart sensors to maintain assets storage premises. However, the company’s main perk is the use of automated guided vehicles to move racks in warehouses autonomously.
Related services and industries
Logistics Software Development
Optimize your entire logistics chain
Build your ideal
software today