Real-Time Inventory Management System
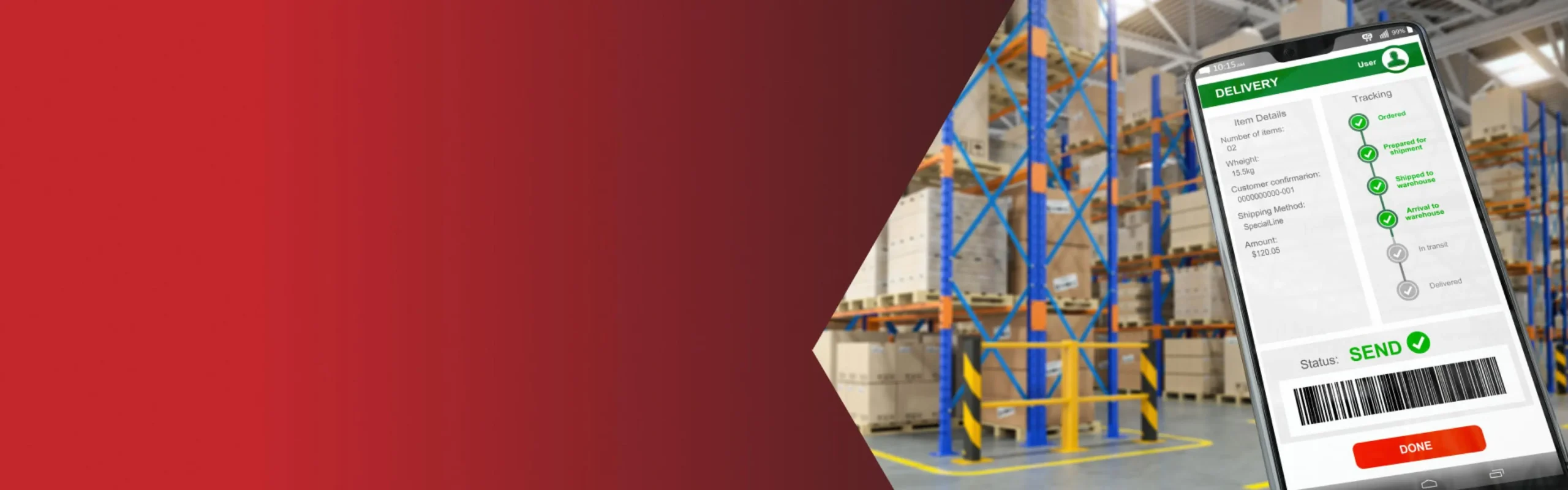


A real-time inventory management system ensures instant data collection, processing, and sharing capabilities.
It helps eliminate the lag of information update, which occurs when applying manual cycle counting.
Statistics say that about 34% of retailers in the US have sold out-of-stock products because of a lack of real-time inventory management. Moreover, over 43% of American businesses track inventory manually using spreadsheets and cycle counting. It results in stockout, excess inventory carrying costs, and inaccurate forecasting.
Real-Time inventory management: basic facts
Real-time inventory management is enabled by advanced technological solutions. They help automatically identify and track packages, pre-process and update inventory data, present information, etc.

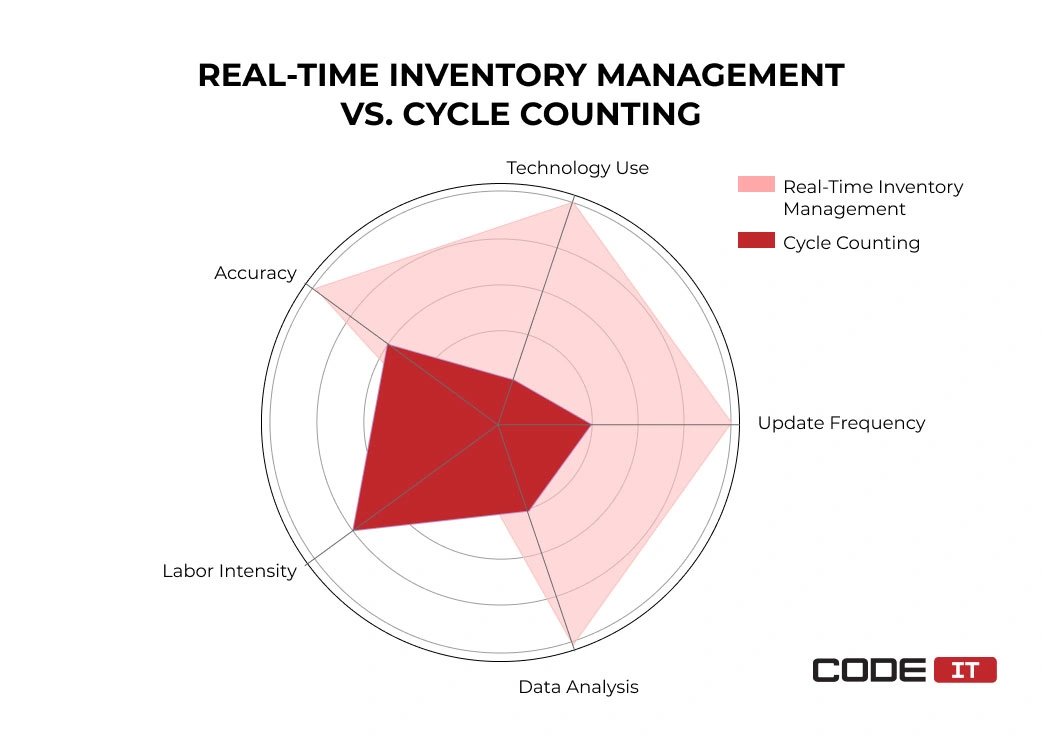
Real-Time Inventory vs Cycle Counting
The implementation of real-time inventory tracking helps enable automation and decrease the manual input significantly. In contrast to manual cycle counting, it helps achieve the following:
- better accuracy
- update frequency
- data analytics
- technology usage
Check out the chart highlighting the strong sides of real-time inventory management compared to cycle counting.
The key peculiarities that help distinguish real-time Inventory and production management software are:
- Simultaneous data update. All the data about in-stock and in-progress inventory is collected and transferred instantly. It may be pre-processed and visualized in time.
- High level of automation. The high level of technology adoption enables real-time data updates. Automated scanners, IoT, and cloud servers are the top tech solutions used in real-time inventory management systems.
- Full inventory and supply chain management. A data-sharing pipeline enables the opportunity to track the location of in-stock inventory. All data updates are delivered simultaneously and displayed on a dashboard.
- Third-party integration. Real-time inventory management software should be connected with ERP, CRM, and other systems to collect data comprehensively.
- Data-driven analytics. Inventory software can summarize and visualize data in live time. With the help of artificial intelligence (AI), businesses can extract valuable insights and forecast demand trend changes.
Technologies
The top eight technological solutions that help enable real-time inventory management include the following.
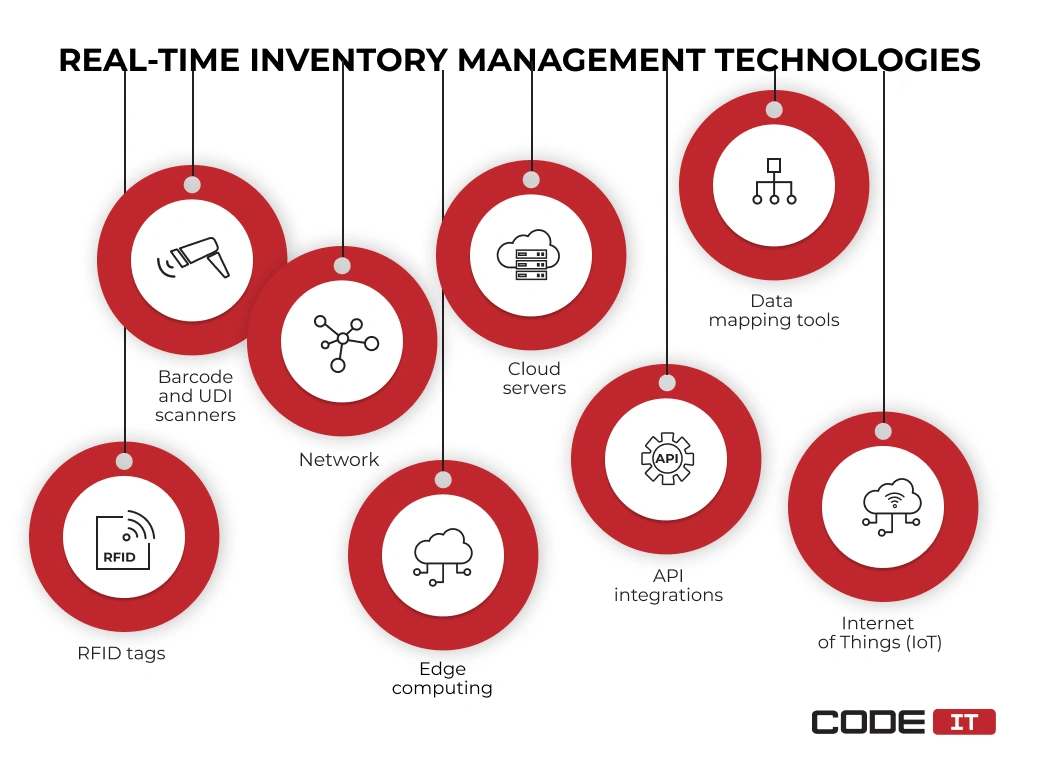
1. RFID tags
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology enables the opportunity to issue and track small tags put on packages. RFID helps reduce stockout costs by ensuring accurate inventory tracking and minimizing shortages.
An RFID tag may contain custom item details, including:
- SKU number
- Serial product’s number
- Name
- Location
- Weight
The amount of data an RFID tag can store varies from several bytes to two kilobytes. The information on tags can be read a few to thirty feet away from an item.
2. Barcode and UDI scanners
Automatic UDI scanners help trace the movement of products. They can scan RFID tags, barcodes, and other UDIs. The scanned data and the item’s location information are sent to a server instantaneously, supporting agile decision-making by providing real-time updates on inventory levels.
3. Network
A network is usually implemented using WiFi routers and wired connections. Other popular technologies for developing a network of devices are Bluetooth, cellular networks, and near-field communication (NFC).
If several networks are connected in a warehouse, it’s advisable to implement a network getaway. It is responsible for device authentication and traffic routing, ensuring predictable order cycles and reducing supply chain disruptions caused by network failures.
4. Edge computing
Additional server nodes integrated into a network present the edge computing layer. They can pre-process inventory data and send commands without transmitting data to the main server.
The implication of edge computing helps:
- reduce the amount of data transferred over the network
- improve inventory data processing speed
- reduce the workload on the main server
- optimize data storage
- improve system scalability
Edge computing helps enable real-time inventory management in large-scale enterprises that need to process large amounts of data without delay. It also supports demand forecasting by analyzing inventory trends closer to the source.
5. Cloud servers
Cloud servers are dedicated computers that can be accessed virtually. They can store and process inventory data remotely. Third-party vendors maintain all the hardware of cloud servers.
All the inventory data collected by a company can be sent to a cloud and processed instantly. The reports and real-time dashboard can be accessed from any location online, helping businesses manage holding costs efficiently.
6. Data mapping tools
The inventory data collected by different devices can have different types and formats. Additional data validation and transformation may be required to enable automatic information flow and analysis.
Data mapping tools can check and transform data in real time. They also enable the creation of custom data transformation rules to connect solutions from third-party vendors. By tracking product alternatives when shortages occur, they ensure that substitution rates are effectively managed.
7. API integrations
Third-party software may be required to connect for gathering inventory and sales data to a centralized repository. The top real-time inventory management system integrations are as follows:
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems
- Customer relationship management (CRM) software
- Point of sale (PoS) systems
- E-commerce platforms
- Vendor and supplier portals
These integrations help maintain backup supplier plans by seamlessly linking alternative vendors to the system.
8. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) in a warehouse describes a set of interconnected smart devices. They help monitor inventory and control storage conditions remotely. All the data gathered by smart devices is instantaneously transferred to the main server. The most popular IoT devices that help enable real-time inventory management are:
- smart sensors
- GPS trackers
- AI cameras
- smart HVAC systems
IoT contributes to warehouse space optimization by tracking available storage capacity and suggesting efficient placement strategies. It also supports first-in, first-out (FIFO) method and just-in-time (JIT) method practices by ensuring timely product movement and replenishment.
Implement the top technologies with CodeIT

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
Benefits of Real-Time inventory management
Real-time inventory management systems enable the opportunity to track all the changes instantaneously.
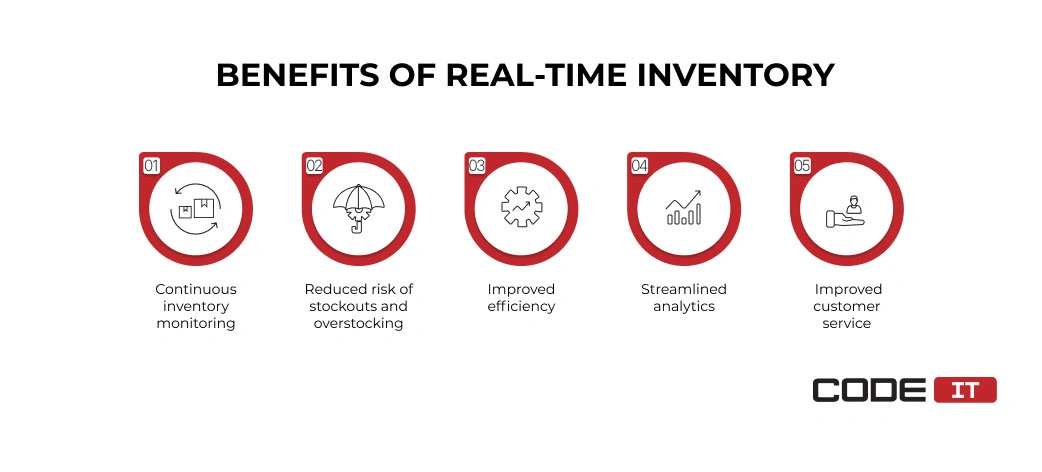
The main benefits include the following.
- Continuous inventory monitoring. Information about inventory levels and products in progress is collected and updated continuously. The main server pings connected solutions to maintain an active connection. New data is sent to the central server when inventory information is updated.
- Reduced risk of stockouts and overstocking. Inventory levels are continuously monitored and delivered to the main server without any lags. Responsible managers can rapidly detect in-stock products that fall below the defined points and submit replenishment requests.
- Improved efficiency. The implication of real-time inventory management helps reduce the manual input and enhance order fulfillment. Technology adoption promotes automation, reduces errors, and helps achieve better inventory accuracy.
- Streamlined analytics. Large amounts of data collected across a supply chain can be summarized and visualized in real time. Artificial intelligence (AI) helps detect hidden patterns and extract valuable insights.
- Improved customer service. The ability to access inventory data in real time and share it with customers/vendors decreases the chance of selling out-of-stock products.
How to implement Real-Time Inventory Management
The adoption of real-time inventory management systems involves the adoption of hardware and software solutions. Also, they need to be connected to a centralized system.
Read about the six crucial steps to implement real-time inventory management.
1. Identify Business Needs and Challenges
Analyze the existing inventory management workflow. Detect bottlenecks or root causes of critical problems. Identify business goals and outcomes you want to achieve by implementing real-time inventory tracking and management solutions. Develop an implementation plan and outline a budget and deadlines.
Roles and responsibilities at the stage
- Stakeholders. Share information about business challenges and objectives.
- Business analyst. Analyze the workflows and business requirements and create a plan. Define functional and non-functional requirements.
- Tech specialist. Analyze existing infrastructure and identify tech capabilities.
2. Pick Solutions and Technologies
Select the most optimal technologies to implement. Pick a tech stack for developing new software and define third-party services to integrate. Ensure that all the hardware and software can be connected to a centralized system.
Roles and responsibilities at the stage
- Solution architect. Pick a tech stack, hardware, and third-party integrations. Select the most optimal infrastructure solution.
- Project manager. Check the scope of work and the documentation.
- Business analyst. Provide assistance in analyzing documentation and business requirements. Communicate with stakeholders upon a need.
3. Integrate Hardware and Develop Software
Onboard a team of developers and engineers. Develop real-time inventory management software and integrate additional services via API. Install the required hardware and integrate it with the software solution. Additional data mapping tools may be necessary to incorporate hardware from different vendors.
Roles and responsibilities at the stage
- Software developers. Create new software systems and integrated solutions from third-party vendors.
- Engineers. Install inventory tracking hardware and configure it.
- Project manager. Coordinate processes and monitor task completion.
Inventory Management System Features
4. Configure a Database and Migrate Data
Install and configure the infrastructure for running software solutions and storing inventory data. Adjust the infrastructure in accordance with the business needs and maximum inventory capacity.
Migrate all the inventory data to a new system. Conduct a comprehensive check to ensure no data was damaged, deleted, or transferred during the migration process.
Roles and responsibilities at the stage
- Software developers. Configure a cloud-based or on-premises server. Migrate inventory data.
- Project manager. Manage infrastructure setup and data migration processes.
5. Test and Optimize
Ensure the developed system works correctly and bug-free. Identify possible flaws in the developed software and fix them. Analyze the system and optimize data processing and sharing workflows.
Roles and responsibilities at the stage
- Quality assurance (QA) specialists. Conduct manual and automated testing. Compose reports on detected bugs.
- Software developers. Analyze reports composed by QA specialists and fix detected bugs.
- Project manager. Manage tasks and monitor team performance.
6. Release and Monitor
Make a new system available for usage. Conduct a workshop to educate staff on using a new system and prepare instructions. Monitor the performance of the released real-time inventory management system to ensure no unforeseen issues occur.
Roles and responsibilities at the stage
- Software developers. Release software and monitor performance.
- Project manager. Manage the go-live process.
- Stakeholders. Conduct acceptance testing.
Inventory Management Software Development Guide
Business-based adjustment
Implementing real-time inventory management depends on a business’s scale. Let’s review the core functionality that small, mid-sized, and large businesses need to implement, considering individual challenges and constraints.
Small Businesses
The foremost challenges that small businesses and startups have to tackle include the limited budget and lack of on-site technical expertise for launching custom real-time IMSs.
Small-sized businesses need to implement baseline functionality, such as barcode scanners and simple allocation algorithms. This helps automate bothersome manual operations and significantly reduces the chance of manual error.
Moreover, it’s advisable to use cloud-based servers for simple infrastructure configuration and real-time inventory management software launch. The usage of cloud-based servers unlocks the opportunity to easily scale operations upon a need, offering scalable options for future growth.
Mid-Sized Businesses
Established businesses need to manage large volumes of inventory, ensuring minimum ecommerce fulfillment disruptions. Also, they often require implementing custom inventory management solutions that are tailored to custom workflows.
Leveraging cloud-based infrastructure, mid-sized businesses can implement custom tech stack integration to connect systems from different vendors. It helps enable cross-platform data sharing, eliminating the usage of isolated solutions. Custom integrations help implement centralized inventory control and monitoring, returns management, and more. Additionally, businesses can track financial records more efficiently by incorporating inventory accounting into their IMS.
Large Businesses
Large enterprises usually utilize complicated inventory management systems across vast sales channels. The solutions for large businesses need to support the management of distributed warehouses to avoid inventory shrinkage in certain locations.
Furthermore, it’s recommended to implement AI-driven systems for optimized planning and demand forecasting. The usage of artificial intelligence helps businesses to analyze large amounts of inventory data and external data to detect hidden trends. Also, the technology helps enable equipment health monitoring and predict when certain machines are about to fail, helping the maintenance team to ensure the minimum downtime.
Challenges in Real-Time inventory management implementation
The development and launch of custom inventory management systems for real time monitoring need organizations to tackle different challenges, depending on their goals. The foremost obstacles that businesses face are as follows.
Development and Initial Setup
It’s crucial to clearly understand business objectives and project requirements to implement the best solutions and avoid excessive spending. A team of stakeholders, business analysts, and tech-strong specialists need to:
- create an architecture for an IMS
- define a feature set
- compose a set of tasks
- define roles and responsibilities
- identify a data flow
Having a backlog of tasks, the development of a custom system begins. Software engineers an MVP and supplement it with new features iteratively. Moreover, it’s required to select the best infrastructure option, considering the unique needs of a business, including system integration with existing platforms.
Cloud-Based Inventory Management
Data Integration
Organizations need to collect large amounts of inventory data from different sources to enable real-time tracking. Moreover, they need to have solid network connectivity to transfer all the records to a central server for further analysis and visualization. The development of custom integrations is required to seamlessly share real-time inventory data across different systems. Consequently, the development of additional data transformation and validation tools may be required to address logistical challenges.
Analytics and Reporting
The raw data collected from sensors using RFID technology and barcode equipment should be translated into charts and custom reports. Implementing custom business intelligence (BI) solutions helps analyze the collected data and display it on dashboards in real time. A data science expert needs to be involved in developing custom dashboards and automated reporting functionality to detect overstocks, stockouts, and shrinkage. Additionally, configuring real-time alerts for critical events ensures teams can react promptly to inventory changes.
Insufficient Expertise
Skills gaps are one of the top obstacles the business faces when implementing custom inventory management software. They need to scout, hire, and manage a team of specialists with strong tech skills and industry-specific knowledge. The lack of skills may lead to the development of low-quality solutions and excessive budget spendings.
Also, it’s required to train your staff when introducing a new IMS, especially in e-commerce and omnichannel retailing environments. The training may require the development of internal guides and learning materials, running workshops, or creating a mentorship program for seamless transition to using a new system.
Real-World examples
The top companies that have adopted real-time inventory management systems and solutions they have implemented are as follows.
| Amazon | Walmart | FedEx | Home Depot | Best Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud-based storage | Electronic data interchange system | Automated barcode and RFID tag scanning | Multiple-storage inventory tracking | CRM software integration |
| AI-driven data analysis | Automated RFID tags issuing and scanning | Start-to-finish package tracking | Predictive analytics for demand change identification | Cloud-based inventory management infrastructure |
| Continuous package tracking | Integrated warehouse management system | GPS-driven real-time inventory tracking | RFID tags tracking for real-time inventory data collection | Real-time data analysis |
| Scanless package identification |
Future trends in Real Time inventory monitoring
Modern inventory tracking systems rely on barcoding or RFID solutions, including barcode scanners, to streamline product identification and movement tracking. These technologies support e-commerce and omnichannel retailing, ensuring seamless order fulfillment and reducing errors in stock management.
The real-time inventory tracking and management keeps evolving at a high pace thanks to the development of new technologies. Below, you will find a list of the five emerging trends to follow and discover what advantages they are expected to deliver.
AI-Driven Data Analysis
Artificial intelligence (AI) and analytics unlock a lot of opportunities for businesses. Using the technology, they can extract actionable insights from large datasets to optimize their inventory replenishment strategies. As a consequence, they can significantly reduce the chance of stockouts and overstocking. AI-driven data processing algorithms can detect hidden patterns, consider seasonality, and analyze external events to develop accurate forecasts. The adoption of advanced predictive analytics further enhances decision-making by improving demand forecasting and resource allocation.
Predictive Maintenance
The collection of the equipment data collected by the Internet of Things (IoT) sensors helps continuously monitor machine health and detect any negative changes. The deep data analysis and reporting of the collected data helps understand when a certain piece of equipment will fail. It helps the maintenance teams to schedule inspection and fixing schedules, achieving the minimum downtime.
Also, the analysis of different data like noise, heat, vibration, and more helps better understand the source of the problem without running complete equipment inspections. Additionally, the system’s adaptability to evolving needs ensures predictive models remain relevant as new data patterns emerge.
Multi-Vendor Cloud Storage
Different cloud providers offer various solutions for real-time inventory monitoring and management. Furthermore, they offer access to diverse pre-built solutions. The multi-cloud architecture of an IMS unlocks the opportunity to access all the useful features offered by different providers, avoiding vendor lock-in.
In addition, it helps businesses cut costs by using one provider for long-term data storage and another one for regular data processing algorithms. A system’s integration capacity plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless operation across different platforms and tools.
Robotics and Automation
The automation of inventory management processes can be achieved by implementing robotics and automation alongside AI user agents. Automated guided vehicles, robotic arms, and other tools can automate tedious and repetitive tasks.
AI-driven user agents can autonomously collect data, analyze it, and make decisions, considering certain conditions and action points. They can continuously monitor the stock level, analyze user activity, identify suspicious stock movement, guide workers, and more. The technology unlocks the opportunity to increase the performance of their team. Gartner says that roughly a third of businesses are expected to implement AI user agents into their workflows.
Conclusion
A real-time inventory management system enables the opportunity to monitor data about products continuously and receive updates instantaneously.
The main peculiarities of real-time inventory are:
- simultaneous data update
- high level of automation
- full inventory visibility
- third-party integration
- data-driven analytics
The adoption of integrated software solutions and automation is required to enable real-time inventory visibility and management. The key technologies include the following.
- RFID tags
- Barcode and UDI scanners
- Network
- Edge computing
- Cloud servers
- Data mapping tools
- API integrations
Enable real-time inventory management

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
FAQ
Real-time inventory software enables the opportunity to monitor all the updates in a warehouse without a time lag. All inventory data flows continuously via defined pipelines.
Real-time tracking is enabled by automatic scanners that track the movement of products in a warehouse. All the data about inventory items’ location and status is sent to the main server simultaneously. It is processed and visualized in real-time by using business intelligence (BI) systems.
Real-time inventory management is enabled by adopting technologies that track inventory automatically. The top technologies that help enable real-time inventory tracking are:
- RFID and barcode scanners
- Cloud servers
- Data mapping tools
- Networks
- Internet of Things (IoT)
Follow the six steps for developing real-time inventory management software.
- Business needs identification
- Tech stack and solutions definition
- Hardware integration
- Database configuration and data migration
- Solution testing and optimization
- System release and monitoring
The core benefits of real-time inventory management are:
- Continuous inventory monitoring
- Reduced risk of stockouts and overstocking
- Increased performance
- Streamlined analytics
- Improved customer service
Related services and industries
Inventory Management Software
Take inventory control, optimize your supply chain, and achieve sustainable growth.
Build your ideal
software today