Top Manufacturing Execution System (MES) Features


A manufacturing execution system (MES) is a digital solution that enables complete processes overview and operations control on a shop floor. The functionality of a MES depends on the variety of modules connected and features implemented.
Customized products help achieve the maximum output by automating processes, tracking all changes, and extracting valuable insights from raw production data. Creating a perfect feature set is one of the core stages of manufacturing execution system implementation.
In this post, you will find the selection of the core MES features and application examples in a real-world environment.

1. Real-time Production Monitoring And Control
It is the crucial feature that enables shop floor workers to get real-time data updates on production, identified issues, flow of material, and more. The development of an Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) network is required for automated data collection from different sources.
All the data is gathered on a central server and processed to deliver crucial information in an easy-to-consume way. Moreover, the use of an IIoT network helps enable centralized operations and control of shop-floor equipment. Users can modify work orders to ensure continuous production or remotely halt operations if any issues are detected, minimizing downtime and maintaining production efficiency.
Feature applications:
- Production tracking software—get real-time data updates on the quantity of manufactured items.
- Machine data collection—use a centralized operations solution to check if your equipment works at its maximum capacity and analyze historical performance metrics.
- Statistical process control—receive instant updates about detected production quality issues and defects, minimizing wastage and downtime.
- Production process and flow control—compare the actual progress to your planned schedule, ensuring that manufacturing processes go under your plan.
- Energy consumption tracking—monitor the consumption of energy in different periods, calculate energy used by idling machines, and identify inefficiencies.
Need a tailor-made MES?

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
2. Quality Management
This MES feature helps ensure that the quality of manufactured products matches the defined standards. A manufacturing system records information about raw materials and processed products. The data can be input manually or collected through automated data collection. When product quality issues are identified, it helps to clearly understand what machines, workers, and processes were involved to narrow down the search for root causes, supporting defect tracking and failure tracking.
Advanced quality management features include automated item inspection using machine vision technology. Machine learning algorithms analyze camera images and detect possible defects automatically, contributing to device history records for improved traceability.
Feature applications:
- Meticulous production tracking—keep detailed records about each stage of production to ensure consistent product quality and enable product genealogy.
- Raw materials monitoring—continuously assess the quality of raw materials from different suppliers and keep records.
- Historical data management—create a database of historical records to analyze the collected information upon a need, supporting failure tracking.
- Real-time quality inspection—analyze real-time data collected from sensors or cameras with machine vision, aiding in-process verification.
- Root cause analysis—get valuable insights into the correlation between certain events and production quality drops.
3. Third-party Systems Integration
The integration with third-party systems facilitates automation thanks to cross-system data exchange and functionality sharing. The key systems to connect to a MES are:
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP) system
- Automation systems (PLCs or SCADA)
- Customer relationship management (CRM) software
- Quality management systems (QMS)
- Inventory management software (IMS)
- Material requirements planning system (MRP)
- Order management solutions
- Supply chain management platforms
The foremost benefits of integrating other systems are optimized workflows, data consistency, and reduced manual input. Users don’t need to transfer datasets between isolated systems or type values manually when using integrations, ensuring smoother manufacturing planning and production planning.
Feature applications:
- Cross-system data sync—connect a MES with ERP software, CRM, and other enterprise systems to always have access to the complete datasets of information using various systems.
- Material flow optimization—automatically share and fetch data from different systems to optimize workflows, improving logistics and shop floor control.
- Seamless communication between teams—bridge gaps between different teams with data sync and automation, benefiting human resources coordination.
- Cost transparency—enables effective cost tracking by synchronizing production data with financial records.
- Equipment health monitoring—collects data from IoT sensors to detect possible issues and predict machinery failures.
ERP & MES Integration
4. Inventory Management And Material Tracking
With this feature, you can effectively trace the consumption of raw materials and always have up-to-date information about the number of produced items. The complete visibility of WIP inventory levels helps optimize stock replenishment strategies, automatically monitor material shelf life and expiration, and reduce waste. The feature also enables the opportunity to meticulously track the movement of serialized products and materials on a shop floor, ensuring track-and-trace visibility.
Feature applications:
- Products and materials monitoring—get real-time inventory updates on the stock levels of raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished products on a centralized dashboard.
- Automated material replenishment—automatically detects when stock levels fall below the defined values and triggers new order creation.
- Material usage monitoring—get insights into raw material usage through different production processes, leveraging in-process data collection for accuracy.
- Item location tracking—receive real-time updates on the location of certain batches and items by using barcode scanners and IoT integration.
- Expiration dates tracking—optimize the management of perishable products and reduce wastage with real-time updates on material shelf life and expiration.
5. Predictive Maintenance
Using the feature, a MES collects and stores maintenance history records about equipment performance gathered by IIoT smart sensors to forecast when a certain machine is likely to fail. Predictive analytics algorithms analyze trend changes over a period of time and build predictive maintenance models by running regular analyses of the collected datasets.
Predictive maintenance helps manufacturers extend the lifespan of machines, and diverse IIoT sensors help better understand the root causes of technical issues and detect critical failures in real-time monitoring.
Feature applications:
- Equipment condition monitoring—track the records about each equipment piece to always have access to complete datasets of maintenance history records upon a need.
- Maintenance schedules creation—develop well-thought-out maintenance schedules, fixing issues in early stages and ensuring the equipment won’t break accidentally.
- Critical issue identification and alerting—automatically analyze key indicators in real time to detect severe changes and notify the maintenance team.
- Maintenance optimization—track the effect of different maintenance activities, components, and lubes used to pick the best ones for extending the lifespan of your machinery.
- Production scheduling and maintenance balancing—use data from different systems to thoroughly plan maintenance activities, achieving the minimum downtime and production processes disruptions.
6. Advanced Planning And Scheduling
The feature enables the opportunity to achieve maximum efficiency by balancing dynamic demand patterns, resources, and material availability. Create well-thought-out production plans and optimised production schedules with no overseen factors that affect the production. The variety of factors analyzed by a MES for thorough planning include:
- Material availability and constraints
- Machine availability, limitations, and tool availability
- Production routing, rules, and workflows
- Deadlines and priorities
- Operator skills and workforce capacity
Moreover, the usage of advanced planning and scheduling algorithms and artificial intelligence helps run simulations to develop the most optimal schedules and work orders. The integration of real-time production data helps develop a feature capable of dynamic planning to achieve the best performance in an ever-changing environment. Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) metrics are used to evaluate and refine scheduling strategies.
Feature applications:
- Production planning optimization—maximize the output and shop floor performance with well-planned schedules.
- Production orders balancing—prevent overproduction or underproduction by balancing production orders and available resources.
- Production schedule adjustment—enable the functionality for making fast adjustments to schedules.
- Order and schedules tracking—collect production data, including information about orders, schedules, and other details, using electronic job cards for better visibility.
- Historical data analysis—process the historical datasets of production data to get actionable insights for future operations planning.
7. Data Analytics And Business Intelligence
Access to actionable insights helps businesses make data-baked decisions that improve shop floor performance and achieve better output. The data analytics and business intelligence feature enables a MES to automatically compose custom reports and dashboards with real-time updates. The visualization feature helps turn raw data into easy-to-consume charts and reports. Moreover, business intelligence algorithms help process large datasets, generating detailed production insights.
Feature applications:
- Real-time updates—collect Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled shop floor planning data in real time and get instant updates on crucial events or emergencies.
- Production data analysis—run a thorough performance analysis of the collected data to identify trends, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement.
- Data visualization and reporting—create a custom dashboard that delivers crucial shop floor updates in the form of charts and personalized reports.
- Insights generation—run production data analysis to identify trends, inefficiencies, and points of growth.
- Trend analysis and forecasting—understand how the demand is expected to change, considering seasonal changes and anticipated one-time events, ensuring product traceability across the supply chain.
8. Workforce Management
Use the feature to effectively manage the workforce to maintain smooth manufacturing processes. Moreover, this functionality of a MES enables the opportunity to assign tasks, track performance metrics, and optimize resource allocation for efficient staff management.
Feature applications:
- Employee performance tracking—collect and analyze certification records and performance metrics on each worker and get detailed reports generated automatically.
- Workforce availability monitoring—get real-time monitoring updates on worker availability, shift schedules, and other crucial details for efficient personnel management.
- Workforce scheduling—enable automated skill-based task assignments, considering the availability of shop floor workers and their personnel qualifications.
- Workforce guidance—integrate task-based access to instructions, helping workers perform their tasks effectively without extended training programs and mentorship.
- Certifications and training tracking—identify skill gaps with up-to-date information on experience verification, completed training needs, and workforce development efforts.
MES System Architecture
Machine Uptime Monitoring Software—СodeIT Expertise
The CodeIT team has extensive expertise in building custom software solutions for businesses in the manufacturing industry.
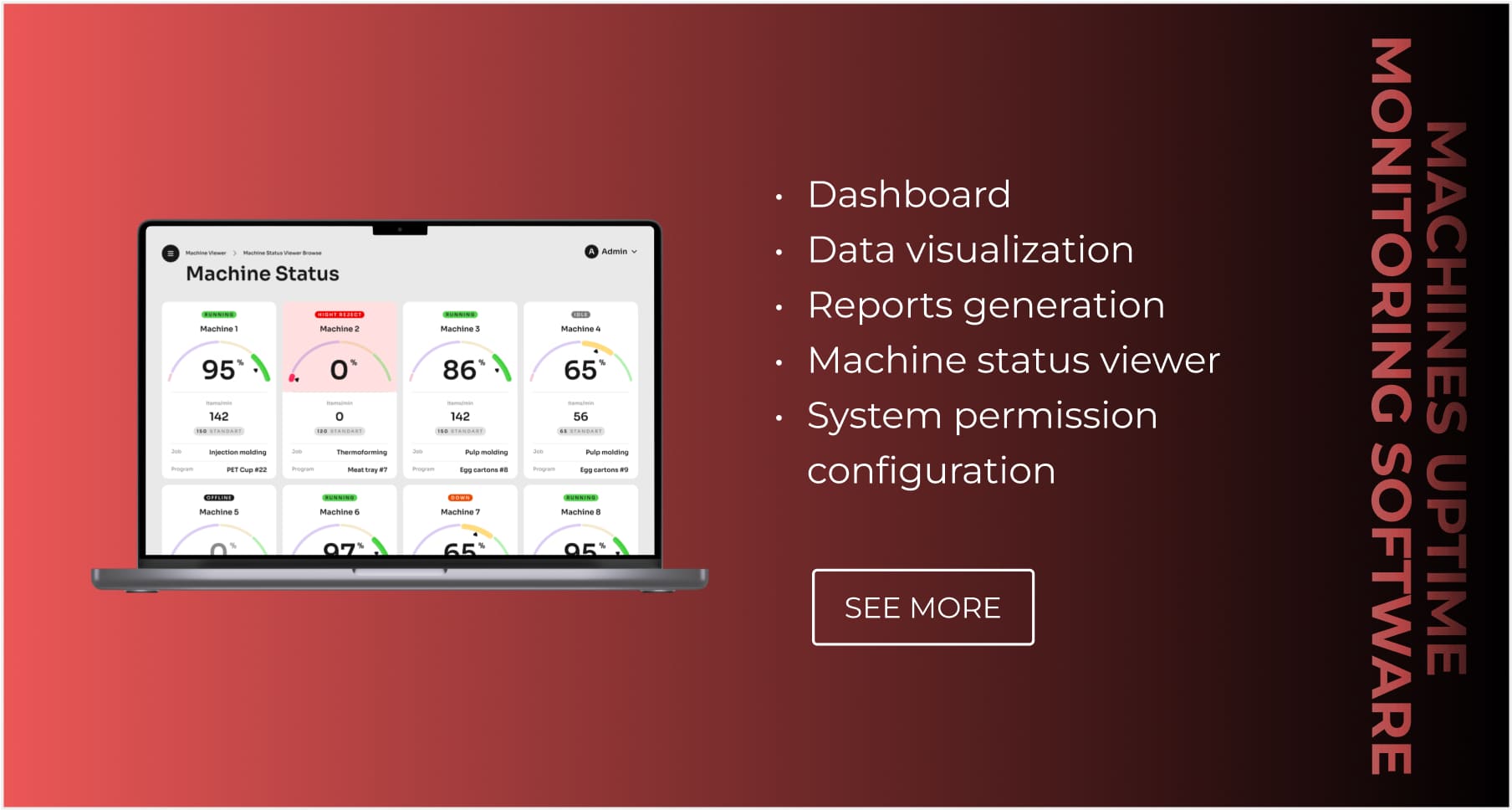
Let’s review one of the solutions developed by our specialists—a tool for monitoring shop floor machine uptime.
Problem
The clients experienced a lack of centralized tools for monitoring the shop floor operations. Hence, the workers had to use isolated solutions and manually transfer data between different systems. The CodeIT team was hired to build a custom solution for collecting and visualizing shop floor data in real time.
Solution
Our software engineers have analyzed the project requirements, selected the best-fitting technologies, and created a solution development plan. We’ve onboarded a team of specialists with the required expertise and implemented the following MES features:
- Dashboard—key metrics from different machines are collected and displayed on a dashboard for quick data access.
- Charting—the system automatically creates custom charts, making the production data easy to consume.
- Reports—custom reports that contain different information are generated by the solution per a user’s request.
- Machine status—users can explore all the machines on a shop floor and examine the actual status of each machine.
- Permission configuration—the admin users can limit the functionality and data access for defined roles.
The developed solution was integrated with the existing manufacturing execution system (MES), enabling seamless data exchange. As a consequence, the implemented solution has helped to increase machine management efficiency by 30%.
Case Study: Machines Uptime Monitoring Software
Conclusion
Developing a custom MES requires a company to identify the needs for building a useful tool for tackling custom needs. Moreover, it’s important not to overcomplicate a system with an extended set of functionalities that are not applicable in a real environment.
The core MES features of a new manufacturing execution system are:
- Real-time production monitoring and control
- Quality management
- Third-party system integration
- Inventory management and material tracking
- Predictive maintenance
- Advanced planning and scheduling
- Data analytics and business intelligence
- Workforce management
Implementing the following features in your MES helps enable the basic functionality for seamless shop floor operations monitoring and management.
Custom feature set for your MES?

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
FAQ
The key features of a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) include:
- Real-time production monitoring and control
- Quality management
- Third-party systems integration
- Inventory management and material tracking
- Predictive maintenance
- Advanced planning and scheduling
- Data analytics and business intelligence
- Workforce management
An MES enhances manufacturing operations by:
- Improving production efficiency—Enables real-time tracking and process control.
- Ensuring product quality—Automates inspections and defect detection.
- Optimizing resource utilization—Balances production orders and minimizes downtime.
- Enhancing decision-making—Provides data-driven insights for process optimization.
- Reducing waste and costs—Tracks material usage and minimizes overproduction.
- Improving maintenance strategies—Predicts equipment failures and extends machine lifespan.
- Enhancing workforce productivity—Automates scheduling and task assignments.
When implementing an MES, manufacturers should consider:
- Feature set—Choose the right set of functionalities to match production needs.
- Integration capabilities—Ensure compatibility with existing ERP, CRM, QMS, and automation systems.
- Scalability and flexibility—Adapt to future business growth and process changes.
- Data collection and security—Establish a reliable IIoT network for real-time monitoring and safeguarding data integrity.
- User adoption and training—Ensure employees can effectively utilize MES features.
- Cost and ROI analysis—Balance the investment against expected efficiency improvements.
Yes, MES solutions can be customized by selecting specific features based on business needs. Companies can implement essential functionalities like real-time monitoring, quality management, and inventory tracking, then expand later with predictive maintenance, advanced planning, and workforce management.
Build your ideal
software today