Manufacturing Execution System (MES) Implementation


A manufacturing execution system (MES) is a digital system that helps monitor and control manufacturing processes. It enables real-time visibility and comprehensive control. Also, it helps reduce errors and enables automation.
The MES implementation is the process of integrating and configuring an out-of-shelf MES software into the existing production line. The MES implementation steps include functional boundary identification, software selection and configuration, and data migration.
Find the full MES integration guide with nine steps below.
Key Considerations
It’s recommended to get prepared before opting for MES implementation services by making the key consideration. They will help you understand what kind of MES solution you need, what outcomes should be achieved, and what implementation approach to use.
1. Baseline and Ideal Outcomes
You need to understand the starting point and existing systems. Review all the floor machines and solutions. Form a clear and comprehensive picture of the current workflows and data-sharing pipelines.
Also, outline ideal outcomes of the manufacturing execution system implementation. The desired outcomes may comprise smart manufacturing or dark production facilities.
Need expert help to start MES implementation?
2. Business Problems
Define the existing business challenges or bottlenecks that decrease your production performance. Create a list of the obstacles and prioritize resolving the most important ones when opting for MES implementation services.
It’s recommended to involve a business analyst in analyzing business processes, eliciting requirements, and understanding the desired outcomes.
3. Realistic Objectives
Adjust your desired outcomes considering the budget, project requirements, and MES implementation capabilities. Set realistic outcomes that you want to achieve when your MES solutions have been implemented.
The set of business objectives to achieve may comprise the following.
- Full workflow control using software accessible from any location
- Improved data quality and production check
- Complete visibility and transparency of the entire production process
- Reduced storage costs for material
- Automated document generation to reduce administrative burden
- Reduced number of lost items
- Improved performance thanks to automated workflow management
Also, setting the “definition of done” for each outcome is advisable to measure results effectively.
MES Implementation Steps
The eight MES implementation steps help automate processes and enable full visibility of manufacturing processes.
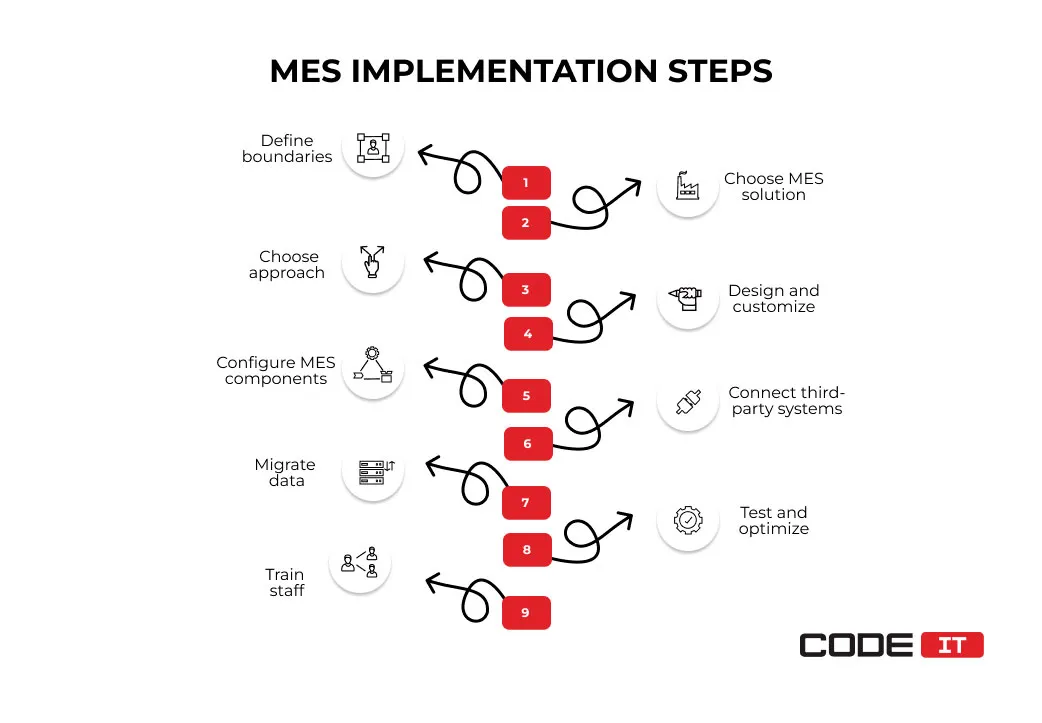
Step 1: Define Functional Boundaries
Analyze floor machines and existing tech solutions that cannot be replaced. Create a list of functional boundaries and tech limitations to consider when selecting manufacturing execution software.
Feel free to use the ISA-95 standards that help understand the hierarchy of industrial automation and control systems.
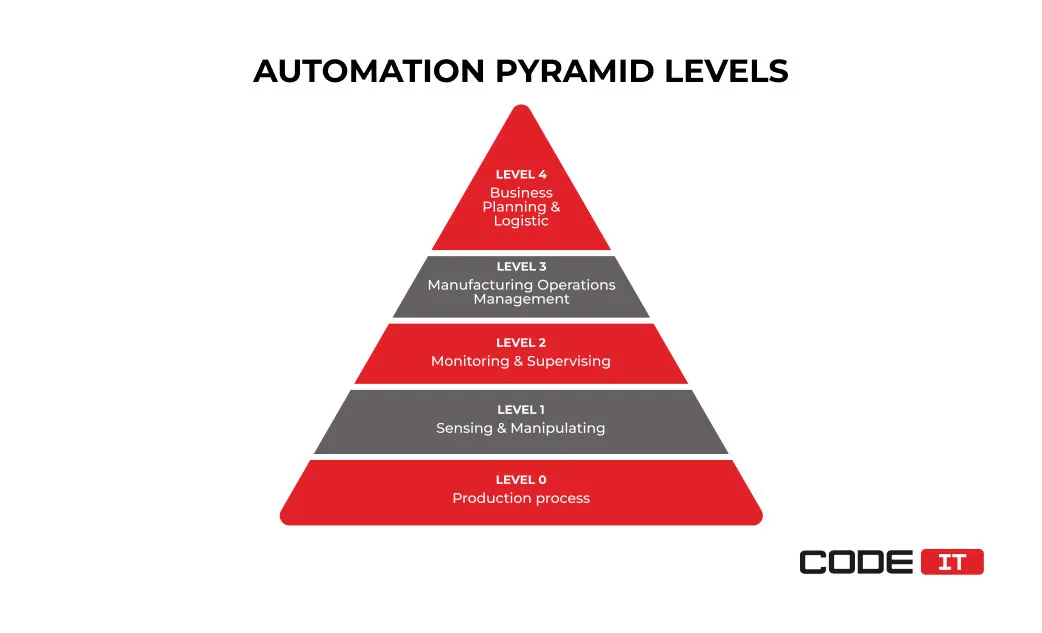
As per ISA-95, the five layers of your production are as follows.
- Level 0: Production devices. Production line machines, materials, products, etc.
- Level 1: Control devices. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) enable basic manufacturing equipment to follow their logic.
- Level 2: Production monitoring and supervision. Devices and software solutions that collect data from devices and are pre-processed.
- Level 3: Manufacturing execution system (MES). Production workflow management that includes maintenance, batch control, inventory management, quality checks, shift management, etc.
- Level 4: Enterprise management. Business planning and logistics. Production scheduling, material usage, storage, shipping, etc.
Access CodeIT expertise to define tech boundaries

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
Step 2: Choose MES Solution
Research and select the best manufacturing execution software to implement. The key factors to consider when selecting are as follows:
- scalability and flexibility
- user interface
- mobile access
- third-party software integrations
- business intelligence solutions
- compliance and security capabilities
- license fees
- user reviews and references
- customer support
Step 3: Choose Implementation Approach
The two MES implementation approaches to choose from are as follows.
- Hiring a vendor. A dedicated company with rich experience building MES solutions will dedicate a team of skilled professionals. They need zero supervision or management. A vendor takes all the risks and delivers final results that need to be validated by stakeholders.
- Hiring an in-house team. You’re responsible for scouting and hiring experts with the required MES implementation expertise. Also, you need to create a detailed plan, create a backlog of tasks, and monitor the progress.
Consider the most suitable option, considering your expertise and available resources.
Step 4: Design and Customize
A detailed manufacturing execution system design is required. The two designs to develop include the following:
4.1 Generic “as-is” MES design
It represents the overall design of a production environment. The generic scheme describes the existing manufacturing processes, hardware, connections between systems, data flow, etc. It’s advisable to categorize all the activities by the four layers.
4.2 Specific “to-be” MES design
Considering all planned changes and improvements, the generic structure “as-is” system design should be updated. Detailed sequence diagrams should be created to describe a new “to-be” model. Tech solutions, data-sharing processes, third-party integrations, and other crucial details must be comprehensively described.
Step 5: Configure Hardware and Software
The three key stages of MES implementation and configuration steps are as follows.
5.1 Configure infrastructure
Set up and configure a server. Choose a cloud-based, on-premise, or hybrid server, considering the project’s needs and requirements.
5.2 Install hardware and software
Implement new sensors, actuators, robotic guided vehicles, and other hardware equipment. Besides, establishing a local network on the production floor is required. A network can be wired, wireless, or combined. Implementing a wireless network is required if employees use tablets or portable terminals.
5.3 Configure MES software
Install the selected MES software and configure it as per the prepared system design. Set user roles and adjust data access permissions. Also, you may configure user agents to automate tedious tasks and enable real-time manufacturing visibility.
Step 6: Connect Third-Party Systems
Integrate third-party software solutions via APIs to extend the functionality of the established manufacturing execution system. Also, integrations help create automated workflows and cross-system data-sharing pipelines.
The key third-party software to integrate includes the following.
- Customer relationship management (CRM) software. Collect user feedback, manage sales, or seamlessly process custom orders.
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. Adjust core business processes with your manufacturing workflows. Enable real-time data exchange to improve process monitoring and decision-making.
- Business intelligence (BI) solutions. Collect data and analyze it. BI solutions help summarize and visualize data. Also, they help extract business insights and identify hidden patterns.
- Supply chain management (SCM) systems. Monitor the flow of goods and synchronize inventory management processes.
- Warehouse management systems (WMS). Manage data storage and retrieval processes. Control storage conditions and adjust them remotely.
Step 7: Migrate Data
Data migration is one of the crucial MES implementation steps. The data migration steps include many activities described below.
7.1 Migration plan creation
Identify data sources by checking all the databases and external systems you use. Categorize and prioritize data sources. Also, identify and label information that shouldn’t be migrated.
7.2 Data preparation
Cleanse all the data and transform it if needed. Ensure you migrate no duplicated or damaged data into a new system.
7.3 Test migration
Run a test by migrating a small amount of data. Check the migrated information to ensure no records are missing or damaged.
7.4 Complete data migration
Execute the complete data migration. The two main approaches to choose from are:
- complete migration
- incremental migration
Step 8: Test and Optimize
Examine the established production planning and execution software and run the following:
- unit tests
- integration tests
- performance tests
Also, stakeholders need to run acceptance testing by thoroughly examining all the functionality in a real-life environment.
Measure the performance of the manufacturing execution system. Discover if data sharing and processing speed can be optimized by reducing spare activities. The main outcome of manufacturing process optimization is a decreased amount of data transferred and stored.
Step 9: Train Staff
Prepare user guides and instructions to educate your staff on using a new manufacturing execution system. Feel free to conduct workshops and presentations for the effective sharing of new information.
Ready to implement MES?

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
Benefits Of MES Implementation
Manufacturing software solutions enable full process visibility and enable process automation. The key MES implementation benefits include the following.
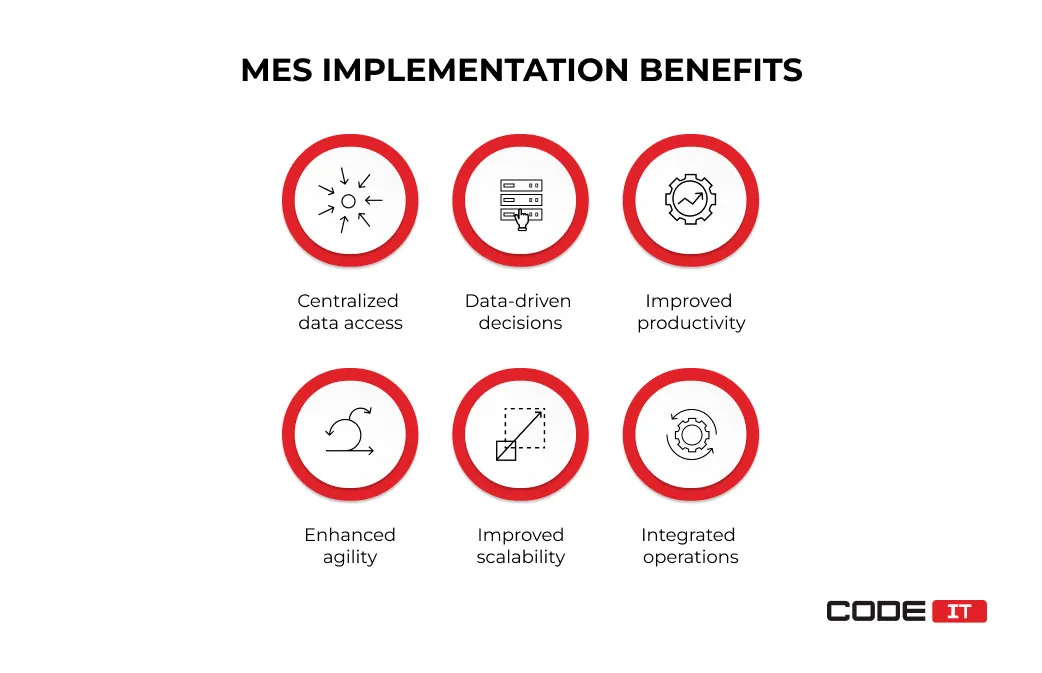
Centralized Data Access
The implementation of real-time manufacturing solutions enables a centralized repository of data. It can be accessed from any location. Also, you can create custom data pipelines to provide employees or systems with the only data access they need to run operations.
Furthermore, using the centralized point, you can issue commands to machines or configure user agents to automate operations. Monitor, pause, or stop processes in a few clicks.
Data-Driven Decisions
All the data collected and stored in one place is a single source of truth. Applying BI solutions and advanced technologies helps extract useful insights from raw data. For instance, artificial intelligence (AI) helps identify hidden patterns and trend changes to run data-driven manufacturing.
Improved Productivity
Industrial automation helps reduce the number of bothersome tasks that require manual input. Moreover, it helps reduce errors, optimize production schedules, identify bottlenecks, etc.
Enhanced Agility
The MES implementation enables real-time access to production floor data and eliminates time lags. Hence, you can discover possible issues or machine failures instantly. Also, you can remotely control equipment for rapid adjustment of manufacturing processes.
Smart manufacturing solutions can monitor all the processes continuously and alert you if any issues or unusual activities are detected.
Improved Scalability
Process automation, digitalization, and integrations with manufacturing solutions help enable rich scalability capabilities. New systems of MES in Industry 4.0 can be rapidly implemented and integrated into the existing solutions.
Integrated Operations
The functionality of digital manufacturing systems can be further enhanced by integrating third-party solutions. You can streamline operations and enable cross-system data sharing. It helps improve the collaboration between different departments.
Challenges Of MES Implementation
The MES implementation steps are related to diverse challenges that need to be addressed, including the foremost listed below.
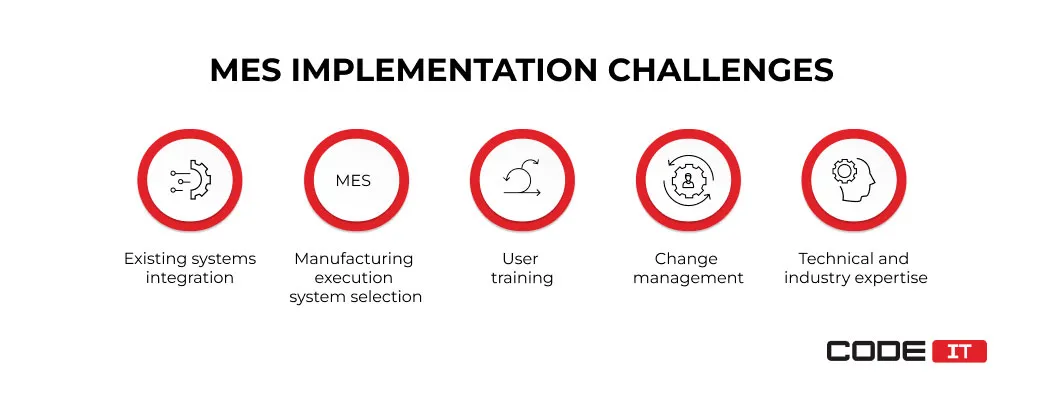
Existing Systems Integration
Manufacturing execution system implementation needs business owners to examine the infrastructure and software solutions thoroughly. It’s crucial to involve tech specialists capable of identifying all technical boundaries. A clear understanding of baseline requirements helps select MES software wisely.
Manufacturing Execution System Selection
There are a lot of manufacturing software solutions available from different MES vendors. Selecting the right manufacturing system requires stakeholders and tech specialists to consider a lot of crucial factors. A misleading decision may cause additional expenses and extended MES implementation time.
User Training
Employee training is one of the crucial factors in the adoption of new MES software. Hence, you need to prepare educational material and instructions for employees. Moreover, you must create a well-thought-out training plan and schedule for each employee, considering their workload and daily responsibilities. Also, it’s essential to assess the skills grasped by employees to ensure they have learned how to use a new MES software.
Change Management
All MES implementation steps need to implement the changes in the existing processes and workflows. It may be challenging to change instructions or implement temporary changes in your workflow management strategies rapidly. Also, poor change management may negatively affect the performance of manufacturing processes.
Technical and Industry Expertise
Advanced expertise in MES implementation is a requirement because you may need to connect many hardware components and manufacturing software solutions from different vendors. Sometimes, additional systems like data mapping tools need to be developed to transform data in real-time.
Implement MES error-free with CodeIT

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
MES Implementation Trends
The top three MES implementation trends that shape the future of manufacturing execution systems are defined by the core aspect of Industry 4.0 and include the following.
1. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The implication of smart devices that are connected to a network streamlines the Industry 4.0 trend. They help enable process automation and continuous control over manufacturing processes. Also, IoT devices help automate warehouse management operations. The most common IIoT devices include the following:
- smart sensors
- robots and actuators
- smart cameras
- trackers
- control systems
2. Cloud Infrastructure
The usage of cloud computing helps enable seamless scalability and security. It eliminates the need to install and maintain on-premise servers locally. Also, remote servers help enable fast and seamless integration of third-party services and remote access to manufacturing execution software.
3. Artificial Intelligence
AI-driven MES analytics provide deep insights into manufacturing processes. They can detect repetitive patterns, identify suspicious activity, and forecast changes.
The technology helps improve decision-making, optimize manufacturing processes, predict machine maintenance needs, etc. AI-powered computer vision can automatically check and assess the production manufactured and submit reports when defects are detected.
CodeIT Expertise
The CodeIT team has completed many MES implementation projects for the top manufacturers in different countries.
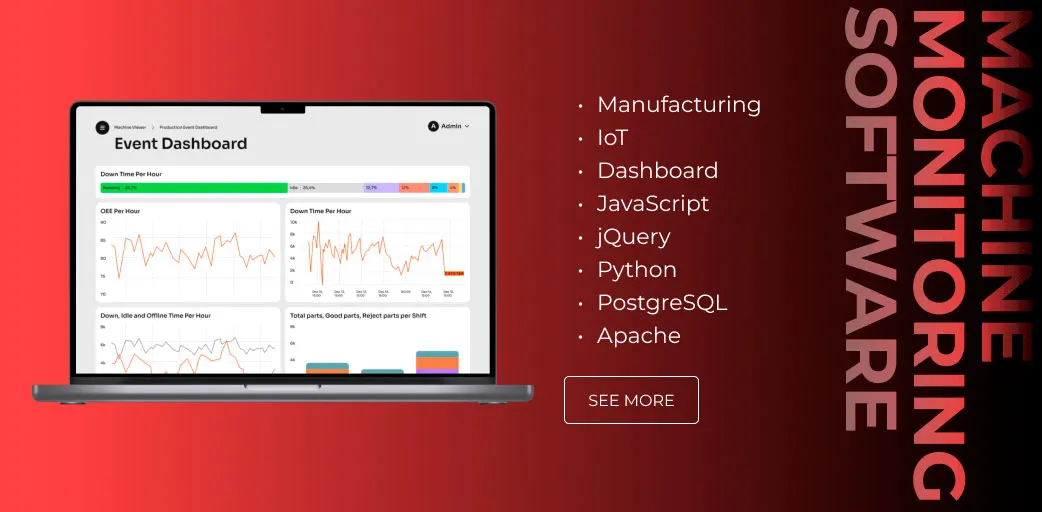
Learn more about the machines’ uptime monitoring software we’ve developed and implemented recently.
Problem
The CodeIT team was hired and tasked with digitalizing the existing manufacturing data. Our specialists were requested to analyze the existing factory floor machines and develop and implement a production monitoring system.
The core problems we had to solve included the following:
- lack of visibility
- insufficient data analysis
- time-consuming report generation
- poor user management
Solution
A business analysis expert has analyzed the existing system and created a detailed solution development plan.
Software engineers have developed a new machine monitoring software from scratch and implemented it. The core features of the created software are as follows.
- Dashboard. A web app that offers centralized access to manufacturing data, reports, and settings configuration.
- Data visualization. All the information collected from production line machines is processed and presented in the form of charts updated in real-time.
- Report generation. The system can automatically generate custom reports and share them.
- Machine status viewer. The current production status of each machine is displayed and updated in real-time.
- Permission configurator. The system offers the opportunity to configure data access permissions for each user role by using checkboxes.
Conclusion
The outcome of MES implementation is a fully functional solution that provides complete visibility and control of manufacturing processes. The core benefits of using a manufacturing execution system are:
- centralized data access
- data-driven decision making
- improved productivity
- enhanced agility
- improved scalability
- integrated operations
The nine MES implementation steps are as follows.
- Functional boundaries identification
- MES selection
- Implementation approach selection
- MES design and customization
- Hardware configuration
- Third-party system integration
- Data migration
- Testing and optimization
- Staff training
FAQ
A manufacturing execution system is a digital solution that connects production line machines. It helps collect data and issue commands in live time.
The nine MES implementation steps include the following:
- Functional boundaries identification
- MES selection
- Implementation approach selection
- MES design and customization
- Hardware configuration
- Third-party system integration
- Data migration
- Testing and optimization
- Staff training
The foremost challenges with implementing a manufacturing execution system are the following.
- Existing system integration
- MES selection
- User training
- Change management
- Technical industry expertise
The primary MES benefits are the following.
- Centralized data access
- Data-driven decision making
- Improved productivity
- Enhanced agility
- Improved scalability
- Integrated operations
The three main manufacturing technology trends are as follows:
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
- Cloud infrastructure
- Artificial intelligence
Build your ideal
software today






