Generative AI in Manufacturing


Think artificial intelligence (AI) running your shop floor still belongs to the future?
This isn’t the future—it’s happening now, and it’s delivering real results for manufacturers.
By automating documentation and improving workflows, AI-powered tools help achieve results like these:
- 95% reduction in documentation search time
- 30% increase in demand forecasting accuracy
- 100% compliance with food safety standards
- 25% cut in maintenance and repair expenses
- 15% reduction in energy consumption
- 8% boost in productivity
Scroll down below to discover how AI is used in manufacturing. Learn more about benefits, implementation strategies, and challenges.
Generative AI Use Cases In Manufacturing
Generative AI can be applied to solving different kinds of problems in a shop floor. It unlocks access to rich data analysis and information management capabilities. The technology eliminates the need to hire specialists in certain fields and increases the performance of employees by providing instant access to the instructions they need.

The top seven generative AI in manufacturing use cases are as follows:
1. Text-to-SQL
The text-to-SQL functionality enables users to submit requests in natural language. AI-driven manufacturing solutions understand users’ intent and translate their requests into SQL code. The code is automatically processed to query and analyze defined data.
A solution delivers data analysis results as requested by a user. Integrating text-to-SQL tools with business intelligence (BI) software enables the automatic generation of custom reports using charts.
Real-life applications in manufacturing:
- Production performance monitoring
- Overall machine health insights
- Inventory management optimization
- Production quality control
- Material and energy usage control
Example: A production manager uses a text-to-SQL AI agent, asking the following question: “What was the output of the assembly line last month?” The system translates the request into SQL code and runs it. Consequently, the solution retrieves the relevant production data and generates a report summarizing output quantities, efficiency metrics, and any anomalies.
Build a custom AI solution for manufacturing

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
2. Document Retrieval
Implementing generative AI in the manufacturing industry helps facilitate document/instruction management and search. A solution analyzes all the internal documentation employees need to use to perform their duties.
They can easily ask an AI agent to find a specific document containing information and retrieve it in seconds. The software provides links to the corresponding documentation and summarized answers based on the only requested documents.
Real-life applications in manufacturing:
- Maintenance manuals and instructions
- Safety protocols and compliance documents
- Standard operating procedures
- Inventory and material handling instructions
- Regulatory and certification documents
Example: A technical team representative asks an AI agent to retrieve technical documents for on-site repairs or machinery adjustments of a defined shop floor machine. The system analyzes the request and pulls out the searched documents instantly from the corporate database.
3. API-Enabled Agent
Integrate third-party software with your custom AI-driven solution so that they can automatically exchange data. API-enabled solutions help manufacturers incorporate industry 4.0 AI technologies into their shop floors. Businesses can automate queries to machines or IoT devices to retrieve operational data and process it.
Automated workflows help improve performance as shop floor workers don’t need to manually collect data and set programs using isolated digital solutions.
Real-life applications in manufacturing:
- Automated production & machine monitoring
- IoT-driven predictive maintenance
- Production planning and scheduling
- AI automation in manufacturing
- Inventory management automation
- Data exchange between ERP and MES
Example: An AI system queries factory machines data in real-time. It analyzes the collected metrics and composes live-time charts. Moreover, it automatically detects performance drops or idling machines.
4. Question-Answering
It is one of the most popular generative AI use cases in the manufacturing industry. An AI chatbot trained on certain documentation can help shop floor workers by providing answers that are based on instructions, corporate rules, and internal documents.
Users can ask questions using natural language in free form. Moreover, the technology enables the opportunity to adjust the answers delivered to users, making them concise or detailed with solid step definitions.
Real-life applications in manufacturing:
- Equipment troubleshooting assistance
- Production process guidance
- Safety protocol enforcement
- Corporate policy and hr queries review
- Training and onboarding support
- Maintenance history and logs
Example: An assistant asks a chatbot to provide safety regulations updates for the last three years. The chatbot analyzes the existing documentation and lists all the updates in safety regulations for the selected period of time.
5. Knowledge Base
Generative AI in the manufacturing industry sets the interaction with a database to a new level. It enables the opportunity to leverage extensive databases of industry standards, best practices, and operational guidelines. An AI system uses the knowledge base information to provide accurate and relevant information upon request. Moreover, it provides links to the original articles so that they can be examined in more detail.
Real-life applications in manufacturing:
- Access to industry standards
- Best practices for equipment setup
- Operational guidelines and procedures
- Product design and engineering standards
- Real-time troubleshooting knowledge
- Compliance and safety protocols
- Training and skill development
Example: An engineer queries, “What are the best practices for quality control in electronics manufacturing?” question. The system retrieves and summarizes relevant guidelines, checklists, and case studies.
6. Real-Time Data Retrieval
Develop data-sharing pipelines to retrieve real-time data on production lines and equipment health. AI agents can analyze real-time data and provide up-to-date insights into shop floor performance, inventory levels, production issues, and more. Moreover, it can simultaneously detect issues and instantly alert responsible managers, describing the detected challenges.
Real-life applications in manufacturing:
- Equipment health monitoring
- Production line efficiency tracking
- Inventory level monitoring
- Predictive maintenance scheduling
- Real-time production issue detection
- Supply chain optimization
Example: An AI-driven system runs real-time monitoring of factory performance or machine wear-and-tear. Any negative changes in machine health that may result in future machinery breakdown.
7. Entity-Linking
It enhances data retrieval and analysis by linking specific entities such as components, materials, and processes to relevant databases and knowledge bases. Moreover, an AI system facilitates more accurate and contextual information retrieval, helping streamline data-driven research and development.
Real-life applications in manufacturing:
- Component tracking and maintenance
- Material traceability and quality control
- Process optimization through data linking
- Spare parts management
- Supplier performance evaluation
- Regulatory compliance and documentation linking
Example: An engineer asks the following question: “What are the properties of aluminum alloys used in aerospace?” The system identifies and links entities like “aluminum alloys” and “aerospace” to its database, retrieving detailed information about material properties, applications, and relevant industry standards.
See what CodeIT’s AI expertise can do for your business
Benefits Of Generative AI In Manufacturing
The advantages of generative AI applications in manufacturing help businesses optimize resource usage and decrease the amount of manual input required to tackle tasks.

1. Improved Operational Efficiency
Optimize manufacturing operations by getting custom shop floor insights. The generative AI in the manufacturing industry helps enable automated data sharing and processing, eliminating the need for shop floor workers to use isolated software. Moreover, it streamlines document management, helping employees to instantly find appropriate instructions and internal guides.
Businesses use the technology’s ability to generate answers to instantly generate custom reports by submitting requests in natural language. Also, the usage of generative AI in manufacturing can provide real-time user guidance by following defined instructions or machinery maintenance manuals.
2. Automation of Repetitive Tasks
One of the core generative AI’s benefits is the ability to automate tedious tasks, allowing human workers to dedicate their time for more complex activities. The integration of smart factories and AI enables data collection for automated production with AI, including quality inspection, equipment monitoring, and basic data entry, and more. Furthermore, the automation of repetitive tasks helps reduce the chance of human error.
3. Effective Data Analysis
The generative AI’s capability to understand a user’s intent and generate code enables the easy running of custom data analysis queries. It eliminates the need to hire a team of data analysis experts and SQL developers.
Custom data analysis enables the transformation of datasets into insights. You can pull specific datasets from various sources and get concise reports in minutes. The thorough analysis of production data helps identify trends and hidden patterns to maintain high machine throughput and minimum downtime.
4. Enhanced Decision-Making
Make data-baked decisions by thoroughly analyzing insights delivered by generative AI. Use chatbots to ask questions and clarify your assumptions. Use your shop floor data to simulate different activities to run scenario planning to pick the best workflow optimization options.
Also, the usage of generative AI in manufacturing for real-time data analysis and visualization helps stay informed about plant floor metrics and unforeseen issues. Instantly generate custom reports on equipment performance, energy consumption, quality metrics, etc.
5. Personalized User Guidance
AI agents can serve as personal assistants by delivering instant answers to any questions. It can briefly describe processes and provide step-by-step instructions on configuring programs or maintaining shop floor machines.
Having access to all the articles in a corporate knowledge base, an AI-driven tool can provide answers that are based on the defined internal instructions and manuals only, avoiding the chance of generating irrelevant responses.
6. Automated Customer Service
Customer support via live chat is one of the foremost generative AI in manufacturing use cases. The usage of chatbots helps automate interactions with clients, guiding them and answering their questions instantly.
Being integrated with third-party systems, customer interactions and support solutions can process user requests and simultaneously provide information about their orders (e.g. actual status, number of items produced, estimated delivery).
Looking for skilled developers with AI expertise?

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
Generative AI Implementation Challenges
The implementation of generative AI in the manufacturing industry requires businesses to create custom plans tailored to their capabilities and business goals. Moreover, they need to solve many challenges, with the following being the foremost.

- Data access and quality—Centralized repositories for the data in defined formats need to be created. Moreover, all the documents need to be checked, ensuring an AI agent doesn’t index outdated or irrelevant information. A company should create a strong document creation and management policy to ensure new information is fully accessible for an AI-driven solution.
- Integration with third-party systems—A business needs to implement data-sharing pipelines, making a system easy to retrieve up-to-date shop floor metrics. The integration challenges software engineers need to overcome include diverse data exchange protocols, custom application programming interface (API) development, and implementation of industry-specific security standards.
- Technical debt—Skilled specialists with extensive experience in the new technology should be involved. The lack of skills for refactoring legacy solutions and developing data-sharing pipelines may disrupt innovation adoption. When technical debt is not addressed, it can reduce agility and make it harder to integrate new AI technologies, leading to performance bottlenecks and increasing maintenance costs.
- Use cases adjustments—Use case development requires manufacturing businesses to thoroughly plan all the activities and map them out so that software engineers can implement all the required functionality. Moreover, they need to review and refine the software solutions if a use case updates by adding new activities or changing the existing ones.
Implementation Strategies For Generative AI
The development and implementation of generative AI in manufacturing may comprise many stages, depending on the existing infrastructure and business goals.
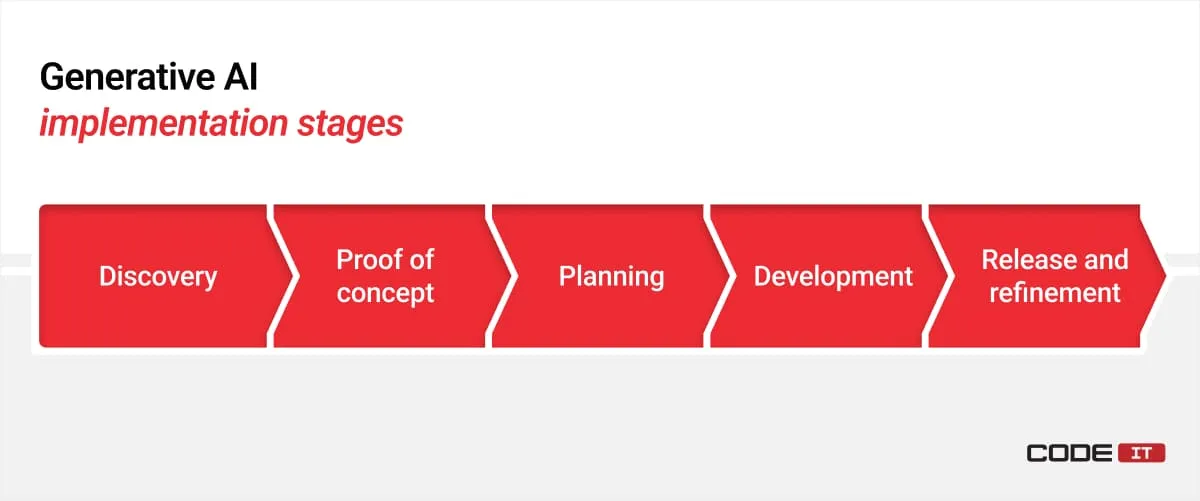
The five key components of AI-driven solution implementation are:
1. Discovery
Review your business process to clearly understand existing challenges and points of growth. It’s advisable to involve a business analyst in the discovery phase to clearly map out all the activities and everything that impacts your business goals.
2. Proof of Concept
Compose a minimum viable product (MVP) with the most crucial features to test your idea. Rapidly create a prototype using pre-built components to use your resources efficiently. Collect user feedback to understand how your AI-driven solution can be improved.
3. Planning
Establish a comprehensive AI-driven solution development plan that comprises all the stages. The foremost artifacts that need to be prepared include:
- Backlog of tasks—a prioritized list of tasks that need to be completed by software engineers and other involved specialists. Each task should be clearly defined and described in detail.
- Estimates—definition of predicted time and resources needed to complete all the tasks. The estimates can be provided in time or user stories.
- Key performance indicators (KPI)—defined measurable values for assessing the performance of software engineers.
- Definition of done (DoD)—a shared understanding of a completed task, comprising detailed descriptions of requirements of each increment that should be met.
- Team set—a document comprising information about tech experts who need to be involved. It should clearly outline the skills and seniority of software engineers.
- RACI matrix—a document that describes all roles and their responsibilities, making the communication and reporting processes straightforward.
- Risk management plan—a list of potential risks that can be faced during the application of generative AI applications in manufacturing, as well as mitigation strategies.
4. Development
The process usually involves incremental software development (MVP + new features that are released gradually). It can comprise the following activities:
- Legacy software refactoring—rewriting the code of outdated software using modern technologies.
- Data collection and preparation—data collection and storage procedures review. Unification of data formats so that it can be easily processed by an AI agent.
- Use case development—definition of specific AI solution use cases and workflows.
- LLM selection and adjustment—the review of existing large language models (LLMs), integration, and configuration as per the developed use cases.
- New software development—incremental creation and release of new features.
- Software testing—unit, integration, and user acceptance testing to ensure a new system works error-free, delivering the required functionality.
- Infrastructure configuration—setting up cloud or on-premise servers to run the developed AI-driven manufacturing solutions and store data.
- API development & system integration—building and integrating APIs to allow the AI solution to interact with other systems and applications.
5. Release and Refinement
The stage includes the deployment of the developed solution and the continuous release of new features to upgrade the functionality. It also includes performance monitoring and troubleshooting of unforeseen issues.
Employee training is also required to ensure that a shop floor staff can properly use the AI-driven software implemented. The training comprises workshops, video guides, and knowledge base creation so that your team members always have access to up-to-date instructions.
Future Of Generative AI In Manufacturing
Generative AI has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing processes, enabling the effective analysis of vast amounts of data and the provision of augmented responses tailored to users’ specific needs.
As per statistics, only 20% of businesses use generative AI in their processes. The others:
- 20% sometimes use gen AI
- 55% rarely use gen AI
- 5% almost never use gen AI
The top statistics that highlight the rapid growth of AI-driven solutions used by businesses are as follows.
- AI is the #1 technology decision-maker in manufacturing plans to implement in the future
- 91% of surveyed manufacturers say that AI is important to future business development
- 82% of businesses plan to increase their AI investments in the future
CodeIT AI Lab
CodeIT has a dedicated AI department with extensive experience in building AI-driven solutions. We build custom software leveraging AI to automate bothersome tasks and enable smart suggestions.
The top AI solutions developed by CodeIT for our clients in the manufacturing niche are:
- AI compliance management tool—monitors regulatory requirements from different sources all around the globe. The AI assistant provides answers, generates summaries, triggers alerts, and more.
- AI documentation assistant—AI chatbot facilitates the operations of technicians and field workers by providing tailored instructions based on internal documentation. It is capable of sharing image- and video-based instructions.
- AI supply chain optimization software—analyzes large amounts of historical data and develops accurate demand forecasts. It also identifies risks and runs what-if analyses.
- AI predictive maintenance tool—collects data from IoT sensors and forecasts when a piece of equipment is likely to fail. Moreover, it guides technicians by providing custom instructions.
- AI vision and QA software—automatically inspects products on lines and triggers actions when defects are detected. Also, it collects product metrics gathered by IoT sensors for deeper analysis.
- AI energy saver—collects data from smart meters, analyzes it, and adjusts the machinery settings to optimize energy usage.
- AI workforce scheduling tool—enables a near-100% shift coverage by running smart analysis of many factors, including employees’ custom preferences, skills, time-offs, etc. It can adjust the schedule in real time when new changes are issued.
- AI talent acquisition and retention software—runs automated CV pre-analysis, selecting the best-matching candidates with the most relevant skills for each job opening. Also, it can automatically schedule interviews with candidates.
- AI waste reduction tool—a set of computer vision, machine learning, and workflow automation helps reduce the volume of waste, saving raw materials and disposal expenses.
- AI changeover optimization tool—helps minimize the time needed to change tools and adjust machine programs, using computer vision, augmented reality, digital twins, and other technologies.
Final Words
The capabilities of generative AI help businesses in the manufacturing industry to streamline processes and improve the productivity of shop floor workers.
Generative AI helps manufacturing businesses improve performance by delegating bothersome and time-consuming tasks to AI-driven tools. The application of AI-driven tools helps businesses to:
- Manage documentation and provide tailored instructions
- Run custom data analysis queries
- Deliver data-backed insights
- Monitor operations and adjust settings in real time
- Analyze image and IoT sensor data
- Build predictions and analyze root cases
The capabilities of AI unlock extensive optimization and automation opportunities for businesses that translate into improved performance and saved expenses.
FAQ
Generative AI in the manufacturing industry helps lower manufacturing costs by automating time-consuming tasks, reducing the need for specialized labor, and providing real-time insights.
The key benefits include:
- 25% increase in productivity
- 70% decrease in breakdowns
- 25% reduction in maintenance costs
The foremost challenges of implementing generative AI applications in manufacturing and ways to overcome them include:
- Data access and quality
- Integration with third-party systems
- Technical debt
- Use case adjustment
The ROI timeline varies based on the complexity of integration and existing infrastructure. Implementing solutions such as real-time data monitoring and predictive maintenance can lead to early savings through reduced downtime and maintenance costs.
The most popular risks associated with implementing generative AI in the manufacturing industry are:
- Data security—AI systems rely on access to internal documents and real-time data, which can be accessed if an AI solution is being hacked.
- System integration vulnerabilities—connecting AI with third-party systems introduces potential vulnerabilities, especially when legacy systems are involved.
The baseline AI implementation strategy comprises the following steps:
- Discovery phase—identify business challenges and set clear AI goals.
- Proof of concept (PoC)—develop and test an MVP to validate the feasibility.
- Planning—outline a detailed integration roadmap, including a task backlog and resource estimates.
- Incremental integration—start with high-impact areas like predictive maintenance and reporting before scaling to other functions.
- Continuous evaluation—gather feedback and refine the solution as necessary.
Build your ideal custom software today