Manufacturing ERP Modules — Basic + Advanced


Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software is a type of digital solution that helps manage various business processes and operations using a centralized service. It automates processes and serves as a shared database. Using cross-system pipelines, an ERP system with the baseline functionality can fetch financial and operational information.
Manufacturing ERP modules exchange data and commands with the core ERP solution. The integration of new modules helps enrich the baseline functionality of a system.
Each module is designed to perform individual actions. The composition of manufacturing modules in an ERP system is custom for each solution and is defined by business needs and processes.
As per statistics, 97% of manufacturing businesses use custom-built ERP systems. They are composed of diverse modules that are aligned with business needs.
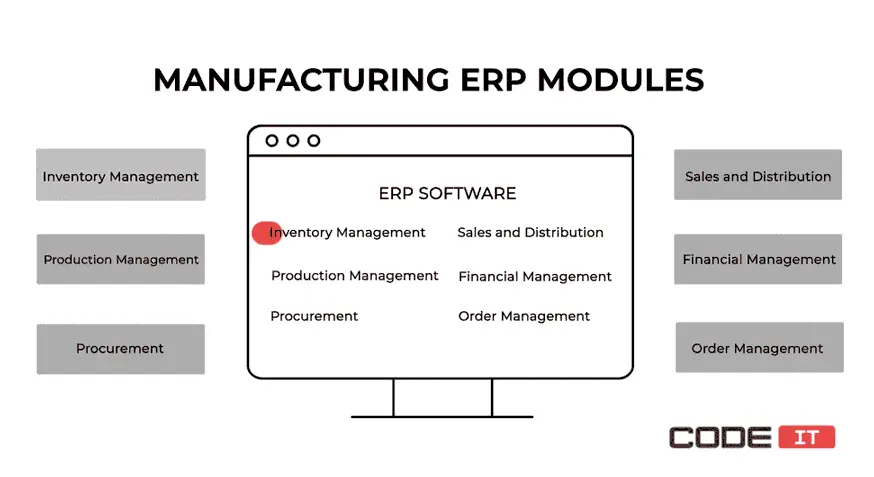
The most widespread ERP modules for the manufacturing industry include the following.
| Basic ERP Modules | Advanced ERP Modules |
|---|---|
| Inventory management | Quality management |
| Production planning and management | Supply chain management |
| Procurement | Customer relationship management (CRM) |
| Sales and order management | Maintenance management |
| Human resources (HR) | Business intelligence |
| Financial management | Workflow management |
| Warehouse management | Marketing |
Basic ERP Manufacturing Modules
The baseline manufacturing ERP software modules are the most commonly integrated. They help provide visibility of the most crucial processes and operations.
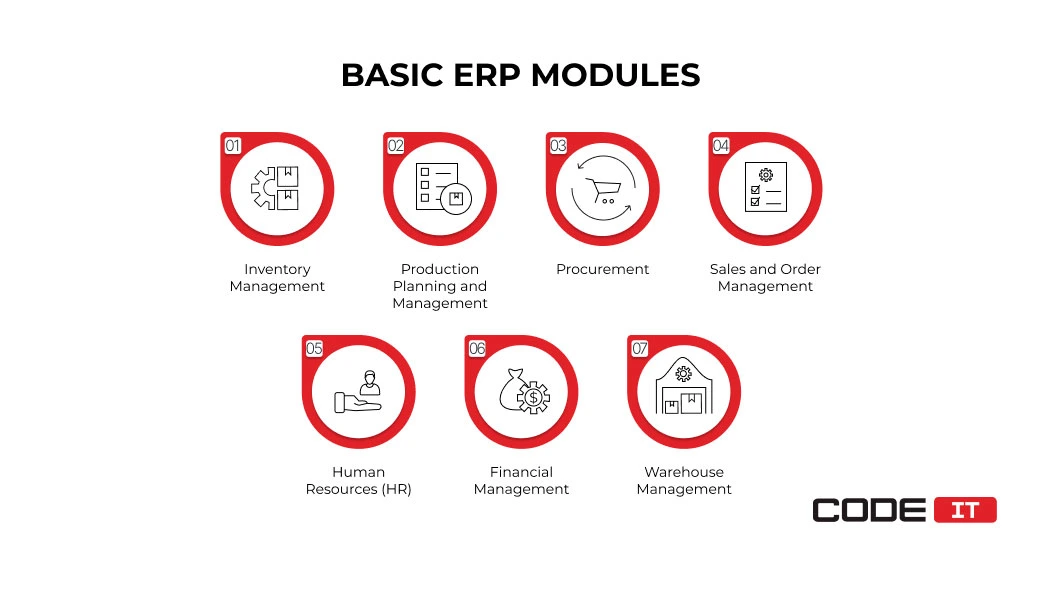
1. Inventory Management
The module integration enables raw materials and manufactured product tracking. Real-time inventory management is enabled by automated barcode and UDI scanning. It helps monitor inventory levels, get real-time updates on work-in-progress, and get alerts of out-of-stock materials.
Module key features:
- UDI scanning
- stock replenishment alerts
- item tracing
- inventory processes analysis
Module implementation impact: Inventory visibility and accurate demand forecasting. Also, the module helps reduce stockout and excess inventory by enabling analyzing processes, monitoring, and manufacturing process optimization.
2. Production Planning and Management
Production process design and activities scheduling. Besides, the manufacturing ERP module helps monitor the resource consumption and production processes. The module enables the opportunity to check, set, and update machine programs.
Module key features:
- machine program administration
- production scheduling
- manufacturing capacity planning
- batch management
Module implementation impact: Enables the opportunity to coordinate manufacturing processes by controlling machine programs. The module implication helps achieve reduced expenses by optimizing production processes and resource utilization.
3. Procurement
Fully control and automate the raw material and product acquisition. The module offers centralized access to information about vendors, quotes, resource availability, delivery time, and other crucial details. Create automated material replenishment orders creation and manage them.
Module key features:
- vendor management
- order processing and update
- contract management
- automation replenishment agents
- analytics
Module implementation impact: Lowered material costs thanks to efficient supplier management. Also, the module implementation helps reduce administrative burden by enabling automated replenishment and vendor-managed inventory management.
4. Sales and Order Management
Top-to-bottom management of sales administration using the eCommerce ERP module and sales order module. Track payments, issue invoices, handle returns/refunds, and monitor work orders and order fulfillment progress for a make-to-order business. The automation implication, driven by the supply chain manager, streamlines sales and item distribution processes with demand planning.
Module key features:
- leads and transactions tracking with serial number and lot number tracking
- pricing and discount management for global, multi-currency, and multi-entity modules
- promotion code issuing and management
- inventory availability check with bill of materials (BOM) integration
- order fulfillment and tracking
- invoice and billing management aligned with production schedule
Module implementation impact: Fast and error-free order fulfillment, management, and tracking. Enhanced order completion visibility with supply chain manager integration with shipping companies. Operational efficiency is enabled by full sales and order fulfillment transparency.
Need tailor-made EPR system?

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
5. Human Resources (HR)
Manage digital records on employee characteristics and hiring processes to orchestrate operations and production management using ERP & MRP systems. The human resources ERP modules manage roles, skills requirements, compensation, and time off.
Module key features:
- employee characteristics information update
- payroll modules and tax data management
- schedule arrangement and update for workforce management
- time off management
- compensation administration with labor cost tracking
Module implementation impact: Helps automate HR and financial management processes and synchronize data with seamless integration across systems. It results in improved employee satisfaction and reduced administrative burden achieved through workforce management optimization.
6. Financial Management
The module is responsible for managing financial operations, transactions, quotes, invoices, etc. Moreover, it helps analyze all the financial data, summarize it, and compose customized reports for supporting decision-making.
Module key features:
- accounting and charting
- invoice review
- cash flow management
- financial planning and forecasting
- custom report creation
Module implementation impact: The module enabled real-time visibility of the financial processes. It helps consolidate data from multiple departments and automates burdening administrative processes. The implications of top-tier technologies help enable data-baked forecasting.
7. Warehouse Management
Control operations for efficient utilization of storage space. Stakeholders can enable centralized facility maintenance and item handling using the manufacturing ERP module.
Module key features:
- inventory tracking and picking
- storage space management
- picking and packing control
- storage environment management
Module implementation impact: The module usage helps achieve smart resource allocation and workflow optimization. It results in enhanced order fulfillment. The implementation of smart devices helps reduce the amount of manual input required for warehouse management.
Read also:
Advanced ERP Modules For Manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing modules in ERP help enable additional functionality. They help automate workflows and reduce administrative burden.
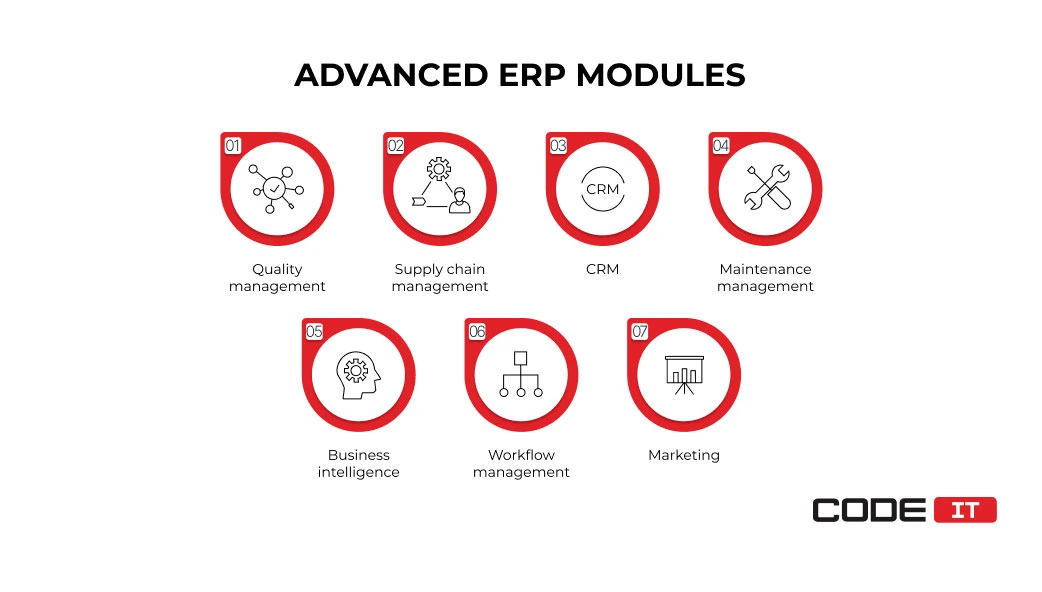
1. Quality Management
The quality control module enables continuous monitoring of the quality of produced items using automated quality control & testing. It integrates quality assurance & control practices into existing production workflows with shop floor control module and PDM module support. It ensures clients receive defect-free products and match established quality standards through formula & recipe management.
Module key features:
- automated defect identification
- standard compliance check
- continuous product quality assessment
Module implementation impact: Continuous quality assurance & control monitoring helps achieve improved product quality. It minimizes recalls and returns. The quality control module enables tracking defects and root causes of production flaws with advanced software features.
2. Supply Chain Management
The comprehensive control and monitoring of the flow of materials and manufactured products. The information includes data about suppliers, contractors, distributors, retailers, and consumers. The manufacturing ERP module helps develop and optimize supply chain strategies, track inventory levels, forecast demand, trace shipping, etc.
Module key features:
- supplier management
- procurement strategy development
- demand planning
- inventory and warehouse management
- shipment tracking
- distributor management
- supply chain analytics.
Module implementation impact: The module enables full visibility and control of materials sourcing, inventory holding, and product distribution. It helps analyze supply chain workflows and optimize processes. Also, the module enables data analysis and demand forecasting to avoid inventory stockouts and overstocking.
3. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Manage interactions with customers and prospective clients using a CRM system. Build trusted relationships with customers and make custom offers to increase sales. Gather feedback to improve marketing strategies and sales funnels through campaign results analysis.
Module key features:
- customer service management
- custom pricing strategies
- sales and marketing activities analysis
- automation of lead generation and management for prospect organization
- customer contact tracking and analysis
- ERP integration for a single source of truth
- cross-department collaboration for streamlined processes
Module implementation impact: Manufacturers can enable personalized customer interactions using the CRM system module. Besides, optimizing lead generation and prospect organization strategies helps increase return on investments (ROI).
4. Maintenance Management
Optimize manufacturing efficiency by enabling predictive maintenance and reducing equipment downtime. Create well-thought-out machine repair and maintenance plans to minimize production downtime.
Module key features:
- machine maintenance scheduling
- equipment data analysis
- asset management
- spare parts and expendable materials management
Module implementation impact: Scheduled equipment maintenance helps reduce line downtime. The analysis of data collected by sensors helps identify anomalies and predict possible equipment failures in advance.
5. Business Intelligence
The module within the business intelligence (BI) manufacturing ERP analyzes large amounts of design data and extracts insights. It provides access to custom tools for visualizing product specifications and generating custom reports with product data management (PDM).
Module key features:
- design data collection and analysis
- charting and visualization of bills of material
- report generation for engineering change orders
- predictive analytics and data forecasting for product lifecycle management
- dashboard creation with centralized control
- revision control for engineering change management
Module implementation impact: The module helps stakeholders make data-backed decisions. It enables access to insights and real-time product specifications using a dashboard. The BI optimizes processes and cuts expenses by defining bottlenecks, problem root causes, and anomalies in product lifecycle management.
6. Workflow Management
The module, integrated with Tipalti finance automation software, manages financial operations, accounts payable, accounts receivable, global payments, and invoices. It analyzes financial data, summarizes it with general ledger consolidation, and composes customized reports for supporting decision-making.
Module key features:
- accounting and chart of accounts management
- paperless invoice processing and review
- cash flow management with real-time spend analysis
- financial planning and forecasting with automatic revenue recognition
- custom report creation for automated global regulatory compliance
Module implementation impact: The module enables real-time visibility of financial processes through digital transformation. It consolidates data from multiple departments with general ledger consolidation and automates administrative processes. The implications of top-tier technologies enable data-backed forecasting.
7. Marketing
This manufacturing ERP module is useful for running and optimizing marketing campaigns. It helps collect and analyze the outcomes of marketing activities. Hence, businesses spend their budgets more effectively, targeting the most relevant audiences.
Module key features:
- marketing campaign management
- lead management
- email marketing
- social media management
Module implementation impact: Detailed analysis of marketing activities helps cut costs and improve lead generation. The centralized data access helps manage multiple marketing campaigns, applying diverse strategies to find the most optimal ones.
Make your custom ERP! Get:
Benefits Of Manufacturing ERP Modules
The top five ERP modules benefits for manufacturing companies are listed below.
As per the research, the average answer confidence rate for the benefits listed below is 75.45%, which is higher than the minimum required rate of 60%.
Reduced Operational Costs
The implication of manufacturing ERP software modules is business management to optimize processes, enable automation, and increase performance. It results in reduced operational costs, including:
- traveling and communication cost
- staff/employee cost
- product delivery cost
- inventory cost
- maintenance cost
Optimized Production Cycling
Using basic and advanced manufacturing modules in ERP software, businesses manage to enable full workflow visibility. It enables the opportunity to identify points of growth and bottlenecks to eliminate.
The top processes optimized by EPR manufacturing modules implementation include the following:
- production
- stock procurement
- report generation
- data preparation
- order checking
- debt payment
Improved Data Quality
Automated data collection and analysis help improve the quality of information. Using established data-sharing pipelines helps reduce loss or unobserved data transformation. As per interviewed stakeholders, the usage of ERP manufacturing modules helps:
- reduce the risk of price miscalculation
- prevent data loss
- eliminate the risk of inputting incorrect data
- increase the accuracy of data
Enhanced Customer Service
Optimized processes help deliver top-tier customer services. The usage of ERP modules for manufacturing helps eliminate the risk of selling out-of-stock products. Also, they enable the opportunity to offer custom-centric services, including personalized pricing strategies and custom order delivery.
The core outcomes of enhanced customer service are defined as the following:
- reduced order cancellation
- minimized the number of order issues
- improved customer satisfaction
- leveling with customers’ needs
Continuous Business Improvement
Using manufacturing ERP modules helps businesses achieve continuous business process improvement by unlocking new opportunities. ERP modules also help improve awareness and collaboration between departments.
The top four continuous business improvements highlighted by stakeholders are:
- job function restructuring
- improved knowledge sharing
- ease of data analysis
- increased employee satisfaction
Build a tailor-made solution! Choose:
ERP Module Implementation Challenges
The implementation of manufacturing modules in ERP is related to challenges that may occur. The three most widespread challenges and solutions are as follows.
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Compatibility issues | Run a technical review and determine the specifications for new ERP modules. |
| Workflow adjustments | Analyze all the workflows and map them out. Create a detailed transition plan, including roles and responsibilities description for new module integration. |
| Data inconsistency | Establish data integrity requirements. Build additional data transformation and validation tools upon a need. |
| Employee training | Create learning materials and run workshops. Implement a custom learning management system to track the progress and assess grasped skills. |
| Vendor lock-in | Build custom solutions and choose open-source pre-built components. |
| Lack of real-time visibility | Implement IoT for seamless data exchange and optimize the existing data handling algorithms. |
Compatibility Issues
The boundaries set by legacy software may affect the ability to implement ERP manufacturing modules. Hence, implementing selected modules may require additional ERP software adjustments or middleware development.
How to overcome this challenge: Conduct a technical review of the existing ERP software for manufacturing to determine the specifications that should be met when selecting a new ERP module.
Workflow Adjustment
Integrating new manufacturing ERP modules requires stakeholders to reengineer existing processes and workflows. It results in the disruption of workflows and unplanned downtime caused by the lack of new instructions.
How to overcome this challenge: Analyze existing business workflows and outline all the changes caused by new module implementation. Prepare a detailed transition plan that includes roles and responsibilities during the ERP model integration. Also, prepare and present new workflows to your team in advance.
Data Inconsistency
Machines and systems generate data in different formats, causing unification challenges when implementing new manufacturing business modules. Hence, businesses need to develop and integrate additional data mapping tools for integrating new modules and building data-sharing pipelines.
How to overcome this challenge: Analyze the existing ERP software for a manufacturing company and define data integrity requirements. Establish strict data validation, transformation, and synchronization protocols before implementing new manufacturing modules in ERP software.
Employee Training
User training is a crucial part of the new ERP module implementation processes. Therefore, it’s advisable to build the UI of new models similar to the legacy solutions to simplify the transition and new software adoption.
How to overcome this challenge: Configure a learning management system for proper training and skill assessment plan is required because of the possible employee resistance for grasping new skills. Also, create step-by-step instructions and run workshops, helping workers understand how to use new software.
Vendor Lock-In
The usage of pre-built components and integrations with third-party vendors may cause strict dependency on other providers. As a consequence, you may experience issues with scaling up your software or adding new functionality.
How to overcome this challenge: Prioritize using custom-built ERP modules with an architecture that fully aligns with your business needs. Also, it’s advisable to choose open-source solutions when using pre-built components.
Lack of Real-Time Visibility
Unoptimized and legacy technologies usage may lead to a significant delay in data transfer. Hence, you may lack real-time insights about the ongoing shop floor operations. Moreover, slow data transformation and transfer may cause production disruptions and shop floor machine idling.
How to overcome this challenge: Implement IoT integrations and optimize algorithms, achieving the maximum data transfer speed. For instance, the implementation of algorithms that transfer data only when the collected value changes helps reduce the load on the central server and network. Also, you can optimize data mapping and validation algorithms for better performance.
Featured Information For C-levels
The implementation of manufacturing ERP modules helps boost operational efficiency and enable AI-driven analytics. The key insights include the following.
- 83% have already implemented enterprise resource and production planning modules
- 97% of businesses use custom-built or customized ERP manufacturing solutions
- 81% say that an ERP system is an essential component for running business operations
- 48% of manufacturers already use cloud-based ERP solutions
- 32% experienced challenges with making EPR systems live
- 43% noticed improved reporting and analytics
- 16.5% is the average costs cut
Case Study
Curious about how CodeIT tackles real-world challenges in the manufacturing industry? Dive into the details of one of our successful projects below.
Problem
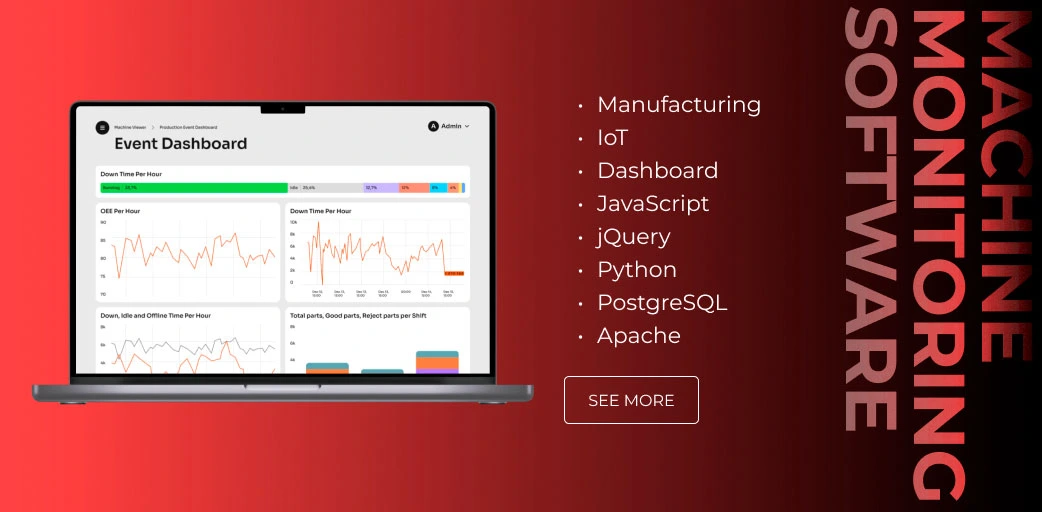
A manufacturing company with a 30-year experience is needed to modernize the production. Stakeholders experienced a lack of real-time visibility of all the manufacturing processes. The client requested our team to develop a machine uptime monitoring system with custom features. Moreover, we had to integrate the developed solution into the existing manufacturing execution software.
Solution
We’ve analyzed the technical requirements provided by the client and created a detailed solution implementation plan. Our team has developed the front-end and back-end machine uptime monitoring software comprising the following components:
- Dashboard. A web application that offers access to crucial information about the shop floor. All the data is updated in real time.
- Data visualization. The data collected from machines is pre-processed and displayed in the form of charts.
- Report generation. Users can generate custom reports to track defined metrics upon demand.
- Machine status viewer. Authorized users can track the status and programs of selected machines.
- System permission configuration. The admin users can set custom data access permission for selected roles.
The developed software has been integrated into the existing manufacturing execution system.
Intrigued by the journey behind the product? Dive into the case study.
Case study:
Conclusion
The integration of manufacturing ERP modules helps enable additional functionality of enterprise resource planning systems. There is a wide variety of industry-specific ERP modules that can be integrated.
Basic ERP manufacturing modules:
- Inventory Management
- Production Planning and Management
- Procurement
- Sales and Order Management
- Human Resources (HR)
- Financial Management
- Warehouse Management
Advanced ERP manufacturing modules:
- Quality management
- Supply chain management
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
- Maintenance management
- Business intelligence
- Workflow management
- Marketing
FAQ
An ERP module in manufacturing is a component of an enterprise resource planning system. It comprises a set of tools for tracking specific tasks. ERP modules help enable automation and cross-system collaboration.
A manufacturing enterprise resource planning (ERP) system is a software application designed to control and manage operations in a shop floor. It is used as a shared database, collecting data from different departments.
The key benefits of implementing ERP modules for the manufacturing industry are as follows.
- Reduced operational costs
- Optimized production cycling
- Continuous business improvement
- Improved data quality
- Enhanced customer service
The main challenges related with the implementation of manufacturing ERP software modules include the following.
- Compatibility issues
- Workflow adjustment
- Data inconsistency
The key trends in implementing ERP modules are:
- 83% have already implemented ERP systems
- 97% use custom-built or customized ERP solutions
- 43% noticed improved reporting and analytics
- 16.5% is the average costs cut
Build your ideal
software today