Medical Practice Management Software Features


Medical practice management refers to handling all organizational activities in a clinic.
On average, 16.6% of the working hours of medical staff are dedicated to administrative activities. Time-intensive administrative tasks may become an overwhelming daily burden if tackled manually. Sometimes, the paperwork burden may consume up to 40% of a clinic’s staff working time.
Medical practice management software (MPMS) enables clinics to automate daily organizational activities to increase performance and improve patient satisfaction.
Below, in this post, you will discover what MPMS is and how it works, what are the features of practice management software, and learn more about medical practice management software requirements.
What Is Medical Practice Management Software?
Medical practice management software helps automate day-to-day operations in clinics. Digital solutions may have diverse functionality that ranges from digital forms to automatic medical billing and coding.
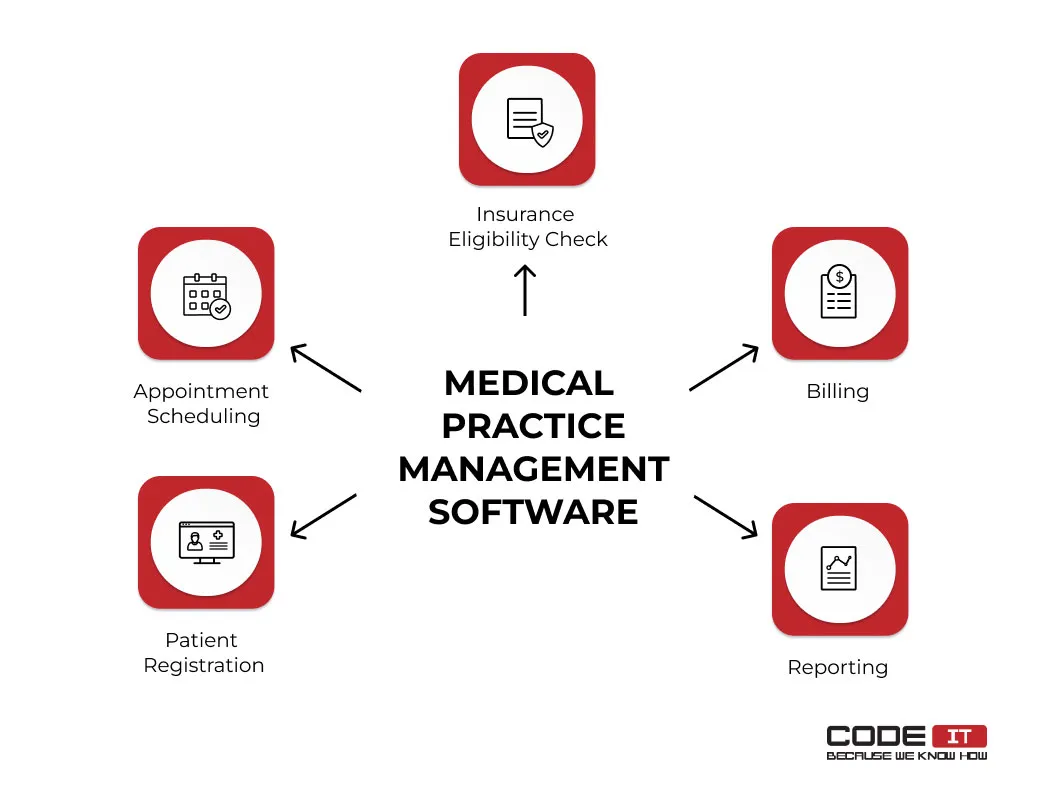
How does MPMS work? It provides beneficial advantages to clinics, insurance companies, and patients. Clinical practice management solutions enable automated workflows to perform administrative activities without manual input.
The core processes that medical practice management software features help automate are:
- Appointment scheduling. Patients can check available time slots and make new appointments online using desktop or mobile devices.
- Patient registration. Administrators can quickly register new patients by fetching clinical data from external resources or scanning documents.
- Insurance eligibility check. Digital systems help check patients’ insurance eligibility and their plans fast.
- Billing. Patient data and medical records are automatically fetched and processed. A digital system helps generate invoices and share them with payers.
- Reporting. Automatic practice analytics delivers regular reports to monitor key metrics.
To get the whole picture, let’s check the implications of medical practice management software in a hospital ecosystem.
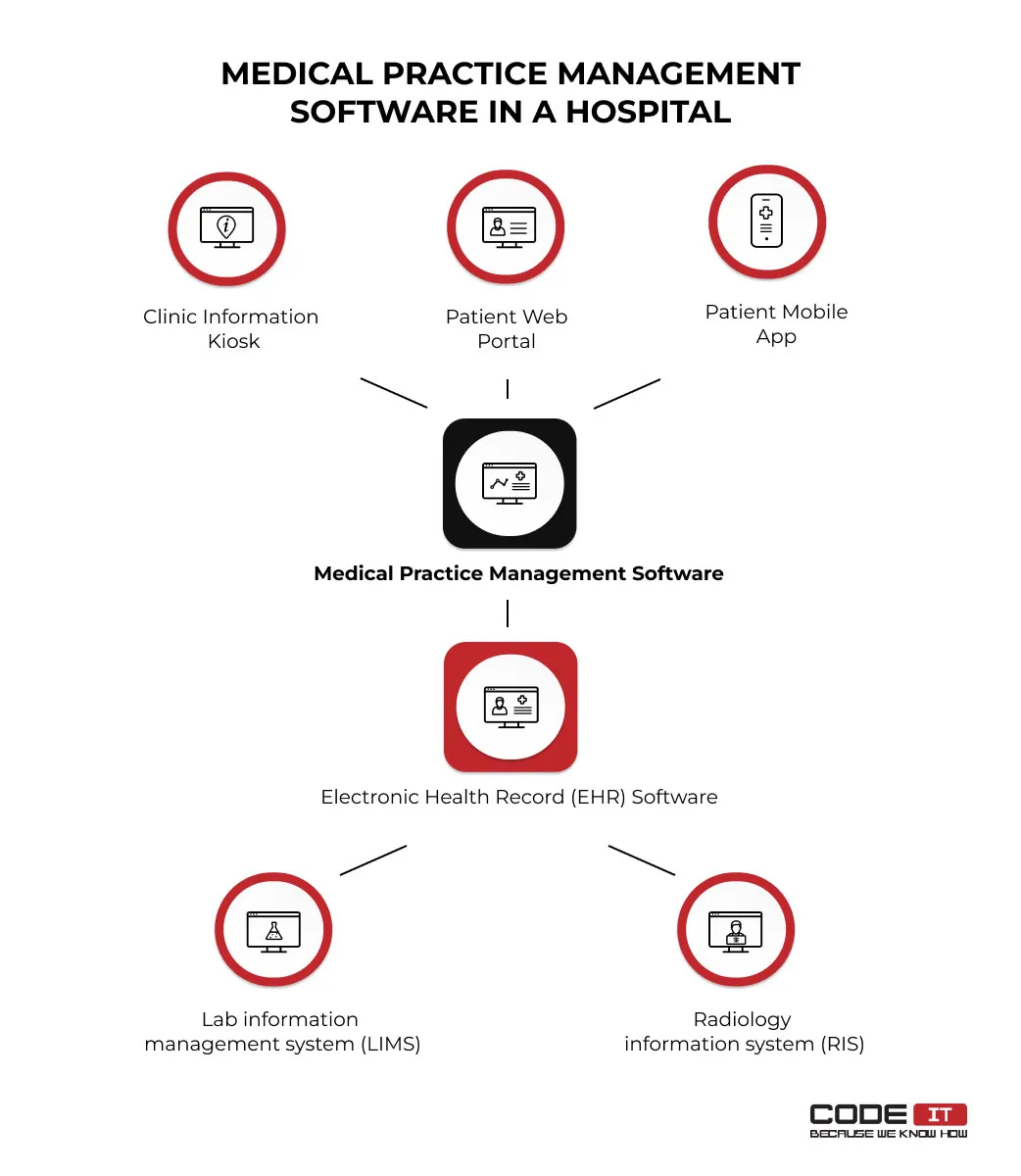
A medical practice management system can be a standalone solution and be connected with other systems to increase its advancement. Usually, it is connected with the following systems.
- Clinic information kiosks provide the opportunity for patients in a clinic to check their appointments.
- Patient portals enable patients to check appointments, change personal information, or communicate with medical staff using dedicated web or mobile apps.
- Electronic health record (EHR) software to quickly fetch information about patients’ past visits, diagnoses, prescribed medications, allergy reactions, etc.
Hire CodeIT to define your medical practice needs clearly

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
What features are available in medical practice management software? Mainly, MPMS is classified as ready-made and custom-built.
- Custom-built software can have a limitless number of one-of-a-kind practice management features developed to match a hospital’s needs. Clinic owners can develop new EHR and practice management software features and upgrade the existing custom-built software solutions.
- Ready-made MPM software has defined feature sets that only vendors can manage. The most popular pre-built medical practice management systems have the following features.
| Software Name | Top Features |
|---|---|
| Pabau | Appointment scheduling, Digital client records, Reminders, Consent forms, Point of sale, Before & After images. |
| WebABA | Online scheduling, Automated billing, Reporting, Mobile app, Paperless document management. |
| TheraNest | Note taking, Custom forms, Staff management, Time management, Appointment creation, Billing, Client portal, Reporting, Telehealth. |
| Luma Health | Patient self-scheduling, Appointment reminders, Waiting list, Mobile check-in, Follow-ups, Patient-provider chat, Insurance verification, Online payments. |
| SimplePractice | Scheduling, Telehealth, Billing, Insurance verification, Client portal, Mobile support. |
Build vs Buy Software
Who uses MPMS? Medical practice management software isn’t an all-purpose solution for medical staff. MPMS is used by the following roles in a healthcare organization.
- Front desk administrators
- Receptionists
- Nurses
- Financial managers
What are the primary benefits of MPMS adoption? The primary goal of using medical practice management software is to streamline administrative processes in medical organizations. Other benefits of integrating an MPMS are as follows.
- Automation of administrative tasks
- Reduced paperwork
- Fast patient registration
- Facilitated appointment creation and management
- Improved billing and claims management
- Simplified document generation
- Improved medical records management
- Improved data quality and reduced duplicated records
- Efficient data analysis and reporting
Medical Practice Management Features
The MPMS software should have basic functionality to streamline administrative processes in a medical organization. Fundamental EHR and practice management software features enable small clinics and individual practice doctors to automate most administrative processes.

1. Appointment Scheduling
Patients can easily check doctors’ availability, pick the best time slots, and make appointments. The basic functionality should enable patients to check, update, and cancel their appointments.
Feature-rich systems foresee the opportunity to send appointment reminders to decrease the no-show rate automatically. Messages can be delivered via email, sms, messengers, phone calls, etc. Also, patients may have access to a waiting list to occupy time slots freed because of canceled appointments.
Problems solved:
- Low patient satisfaction — An online booking system enables the opportunity for patients to choose a time slot, reducing the time spent in a waiting room.
- Increased costs — Automated reminders help keep people updated about upcoming appointments, reducing the no-show rates.
- Manual error — Automated data collection and management helps reduce the required manual input, reducing the chance of error.
Feature application example:
A clinic uses the online booking feature to help patients pick the best time slots for screening. The feature delivers automated reminders via email and SMS.
2. Patient Registration
It enables clinic staff to quickly find, input, and fetch data from external resources. The functionality should grant access to a database of patients, their past visits, diagnoses, etc.
Using advanced components of the patient registration functionality, a clinic’ staff can:
- create customizable registration forms
- scan and digitize documents
- verify the identity of patients
- create and share consent forms
- fetch data about patients from third-party platforms
Problems solved:
- Paperwork — the patient registration feature helps automate workflows and pre-populate data, reducing the paperwork burden of the medical staff.
- Poor data accuracy — A digital system ensures accurate and consistent patient data. It can be easily shared between departments. Moreover, the medical staff can track changes in patient records.
- HIPAA guidelines violations — The usage of a custom-built digital system helps ensure HIPAA compliance and other regulatory medical practice management software requirements.
Feature application example:
The digital registration solution allows patients to submit their information remotely. It also fetches data from external sources to pre-populate information automatically.
3. Insurance Eligibility Check
The insurance coverage availability check is a daunting option requiring significant manual input, depending on the provider. A digital system can help automate the majority of processes by using the following solutions:
- insurance provider information submission form
- electronic insurance eligibility verification
- access to the information about patients’ coverage plans
- API integrations with top health insurance providers
Problems solved:
- Increased costs — The feature helps reduce billing errors, leading to optimized spending.
- A large number of errors — Automated verification and reduced administrative burden help minimize the risk of error.
- Manual workload — The automation of tedious tasks and streamlined practice workflow management help reduce the required manual input, optimizing the performance of administrative staff.
Feature application example:
A medical center utilizes the feature to automatically verify insurance eligibility. The feature automatically checks coverage with major providers by analyzing the information input by the medical workers.
4. Billing and Invoicing
With the help of medical practice management software features, a clinic’ staff can use the collected information about patients’ coverage plans to compose invoices. A digital system can automatically analyze data about services offered by a medical organization to automatically compose:
- claims to insurance companies
- bills to patients for non-covered services
Digital solutions help medical staff reduce the number of errors and track payments effectively.
Problems solved:
- Financial reporting burden — Access to accurate billing data helps in creating reliable financial reports.
- Patient dissatisfaction — Transparent billing and invoices help avoid confusion and disputes over charges.
- Human error — Process automation helps reduce the chance of manual error.
Feature application example:
The feature automatically generates invoices based on services provided. Also, it helps automatically submit claims to insurance companies and tracks payments.
5. Reporting and Analytics
Automatic reports provide clinics’ management with complete visibility of all the processes. A digital system can automatically analyze different metrics, compose reports, and share them with those defined personnel.
Different types of reports containing diverse information can be shared with various roles in a clinic. The foremost details that generated reports can comprise are as follows.
- Financial metrics: information about income, expenses, services offered, accepted & rejected claims, submitted invoices, and other crucial financial metrics.
- Patient data: anonymized information about location, average age, gender, diagnoses, treatment procedures, satisfaction rate, etc.
- Appointment details: summarized scheduling data, including the number of visits, rescheduled & canceled appointments. Also, reports can indicate the average no-show rates, waiting time, types of appointments, and other details.
- Employee performance: information about the number of visits per day to defined doctors, average visit duration, patient outcomes & satisfaction, etc.
Systems with advanced practice management features can help medical staff simultaneously get custom reports that include data of defined ranges or match only picked criteria.
Problems solved:
- Big data analysis challenge — The implementation of business intelligence helps healthcare providers turn large datasets into insights.
- Poor operational visibility — The feature provides useful insights into operations, highlighting inefficiencies.
- Insufficient performance monitoring — Custom reports are composed automatically, and real-time charting helps meticulously monitor the performance of workers.
Feature application example:
The business intelligence functionality helps a clinic to analyze all the data and generate dashboards that update charts in real time. It provides insights on patient demographics, appointment trends, financial performance, etc.
6. Messaging
It is one of the advanced medical practice management software features that enables medical staff to communicate with patients, insurance providers, and doctors seamlessly. The messaging functionality can help medical staff to get the additional information and clarify details by contacting other people via different sources.
Problems solved:
- Communication gaps — The feature helps enable smooth and convenient communication between patients and medical staff.
- Lack of patient engagement — It helps run real-time interactions, improving patient satisfaction and engagement.
- Challenging employee training — The establishment of clear communication channels and defining roles & responsibilities helps streamline employee training.
Feature application example:
A healthcare provider uses a communication platform that foresees the opportunity for doctors, nurses, and administrative staff to communicate and share files across different departments.
7. Integration with Other Systems
The integration with systems like electronic health record (EHR) systems helps clinical staff access information about patients remotely, including the following:
- patient demographics
- medical history
- lab test results
- allergy information management
- prescribed medications
- insurance information
Medical data can be fetched from other systems automatically to speed up the registration process and simultaneously access crucial patient information.
Problems solved:
- Usage of isolated systems — The integration and cross-system data sharing help avoid the need to manually import/export information using software solutions from different vendors.
- Limited data access — It provides instant access to all patient data, eliminating the need to submit requests to different departments to obtain the required information.
- Inefficient workflows — Streamlined data access helps optimize workflows and enhance the efficiency of medical staff.
Feature application example:
A hospital has integrated the MPMS with lab and imaging software. The integration foresees the ability to automatically fetch medical images and access lab integration to get results when they are ready without submitting any requests.
8. Patient Portal
A dedicated portal helps improve patient satisfaction by offering instant access to crucial information and self-service functionality that offers the opportunity to:
- check, reschedule, and cancel appointments
- update personal information
- communicate with a clinic’s personnel
- request prescription refill
- access educational resources
- fill in medical forms and share feedback
An advanced patient portal should be accessible using mobile devices. It can be a mobile app or a mobile-optimized web application.
Problems solved:
- Dissatisfied patients — The self-service functionality helps improve patient engagement and satisfaction.
- Inaccurate patient data — The patient portal enables patients to update their personal information and double-check if the data is accurate and error-free.
- Violated HIPAA guidelines — The feature offers secure access to personal health information.
Feature application example:
A medical institution uses a patient portal accessible via a browser. The portal enables patients to view their medical records, request prescription refills, communicate with healthcare workers, etc.
9. Electronic Prescribing
Electronic prescribing is one of the advanced components of medical practice management software that provides a clinic’s staff with the opportunity to:
- check patients’ medical history
- check allergy reactions
- prescribe new medications
- accept/decline refill requests
- submit dispensing requests to pharmacies
Problems solved:
- Medication errors — Electronic data management helps minimize prescription errors and improve the accuracy of information.
- Low patient satisfaction — The feature helps speed up the prescription processing, which results in improved patient satisfaction.
- Labor-intensive workflows — Automation helps minimize the number of bothersome and repetitive tasks.
Feature application example:
A hospital uses the electronic prescribing feature to send e-prescriptions directly to patients’ preferred pharmacies. Moreover, the system automatically checks for drugs and allergies.
Create software with an ideal feature set from scratch

Business First
Code Next
Let’s talk
MPMS Requirements And Mandatory Components
Defined medical practice management software requirements should be met to work without downtime. Let’s check the obligatory requirements below.
Hardware Requirements
The four most popular options for installing MPMS are:
- Local desktop. An application runs on a dedicated computer in a clinic. All the data is stored on its hard drive.
- On-site server. An app runs on an on-premises server. Medical staff can access its functionality using desktops connected to a local network. Data is stored on physical hard drives in a clinic. A medical organization maintains all hardware and software.
- Cloud server. Remote servers run medical practice software, and data is stored in a cloud-based software. Medical staff can access the software and medical data using desktops connected to the Internet. A third-party company manages all the hardware.
- Hybrid server. The combination of on-site and cloud servers that are connected into one system.
All the options have distinctive peculiarities considered by medical organizations, depending on their needs.
On-Premise vs Cloud Hosting
Every option needs clinics to supply medical staff with a sufficient number of desktops. However, the other hardware medical practice management software requirements may vary.
Let’s take a close look at the technical medical practice software requirements.
| Local Network | Internet Access | Hard Drives | Backup Server | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local Network | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| On-Site Server | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Cloud Server | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Hybrid Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Depending on EHR and practice management software features, a clinic owner may be required to install and connect additional devices, like:
- scanner and printer
- barcode scanners
- point-of-sale (POS) machine
- cameras
- biometric devices
Software Requirements
Medical practice management software requirements vary depending on a selected option. In the case of using out-of-self software, vendors provide detailed software specifications. Custom-built solutions can be tailored according to your existing infrastructure or specific requirements for medical practice software.
Most practice management systems require medical organizations to have an operating system (OS) and web browsers installed on desktops. Servers should have dedicated operating systems and database management systems installed.
Regulatory Obligations
Depending on the location of a clinic, many regulatory obligations to patient data management may apply.
In the US, all medical institutions should comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). It defines solid rules that clinics need to follow to collect, store, and share sensitive patient data securely. Adherence to HIPAA rules helps reduce errors, protect patient data, and effectively respond to breaches.
Medical Data Interoperability
Data interoperability helps ensure different systems can exchange and interpret clinical data error-free. A medical practice management system should support backward-compatible medical data interoperability standards to send requests and fetch information from other systems.
HL7 Standards To Enable Medical Data Interoperability
Security Requirements
It’s vital to keep patient data safe by enabling the following security features.
- Role-based data access. Different roles can access only defined types of medical data. Access to restricted data should be approved by responsible managers.
- Automatic data backups. Crucial patient data should be automatically backed up. Backups need to be stored on dedicated devices.
- Encrypted information. End-to-end encryption keeps patients’ sensitive information safe in case of breaches.
- Response plans. A defined set of activities to effectively tackle unforeseen issues that lead to data loss.
Things To Consider When Implementing A New System
Whether an out-of-shelf or custom-built software is considered, the following steps help implement a new solution.
1. Planning. Prepare a detailed plan for implementing new EHR and practice management software features. It’s recommended to define time frames, deliverables, and roles to involve
2. Data migration. Configure the best option to migrate patient data from spreadsheets or a previous system to new software.
3. Staff training. Create learning materials and define skills that should be learned by medical staff. Also, you can conduct a workshop and create a detailed learning plan to train staff efficiently.
4. System maintenance. Monitor the performance of new software and upgrade it to increase the computing power and disk space upon a need. Also, it’s necessary to troubleshoot technical issues rapidly.
Key Takeaways
Small medical practice offices and large clinics widely adopt MPMS software. According to statistics, the global medical practice management software market is projected to double its size from 2022 to 2029, with a CAGR of 9.30%.
The core components and medical practice management software requirements are as follows.
- Hardware requirements define the technical specifications of servers, desktops, network equipment, and other devices to install.
- Software requirements define supported operating systems, browsers, and obligatory-to-install tools.
- Regulatory obligations define data processing and maintenance rules to keep sensitive information safe.
- Interoperability enables error-free health information exchange between systems that use different technologies.
- Security requirements define a set of measures that help keep patient information safe and rapidly respond to unforeseen issues.
The list of the most popular medical practice management software features includes the following:
- appointment scheduling
- patient registration
- insurance eligibility check
- billing and invoicing
- reporting
- messaging
- integration with other systems
- patient portal
FAQ
Medical practice management software (MPMS) enables clinics and healthcare organiNozations to automate daunting administrative tasks and paperwork. Using MPMS, hospitals can automate patient scheduling, registration, invoice creation, insurance eligibility check, and many other processes.
MPM software may imply a large number of distinctive features. The most popular ones are:
- appointment scheduling
- insurance eligibility check
- billing and invoicing
- reporting
- messaging
- integration with other systems
- patient portal
The automation of daunting processes helps medical organizations streamline administrative processes and increase the performance of medical staff. The core benefits of adopting MPMS are:
- administrative tasks automation
- reduced paperwork
- rapid patient registration
- simplified appointment creation
- enhanced billing and claims management
- improved medical data quality
The minimum hardware & software specifications for MPMS depend on selected out-of-shelf or custom-developed solutions. Usually, the medical practice software requirements are as follows.
- Hardware requirements: a cloud-based or local server, desktops, network equipment, external devices, etc.
- Software requirements: desktop and server operating systems, web browser, database management software.
Yes. Medical practice management software can be connected to different systems, including the following:
- Information kiosk—to check existing appointments in a clinic
- EHR software—to rapidly fetch and write patient data
- Patient portal—to enable patients to manage their appointments and personal data
Using medical practice management systems, medical staff can compose custom reports by analyzing selected metrics. Some types of reports MPMS can create are:
- financial reports
- patient demographics
- appointment statistics
- employee performance
Some MPMS vendors provide their clients with staff training and technical support, while others don’t.
If you develop custom-made software from scratch, you must prepare training material and conduct workshops.
Build your ideal
software today